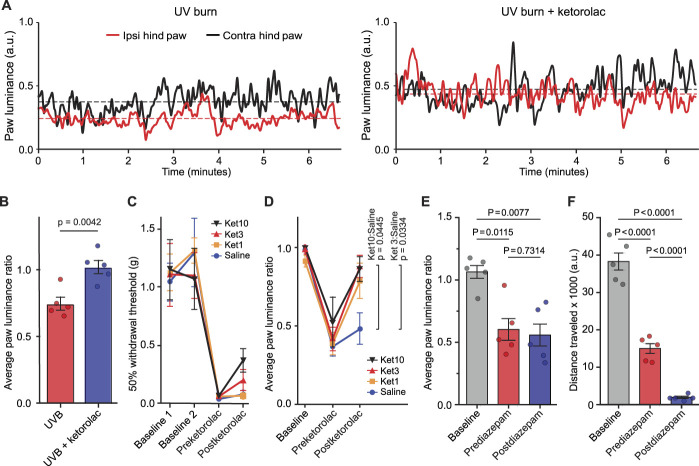
Figure 4.
Average paw luminance ratio evaluation of analgesia in the inflammatory pain model. (A) Paw luminance signals of an individual animal show mechanical hypersensitivity in the injured paw (left hind paw) induced by UVB (left panel) detected by reduced luminescence and increased luminescence as a measure of the analgesic effect of ketorolac (10 mg/kg, right panel). (B) Ketorolac 10 mg/kg recovered the average paw luminance ratio in UVB mice to control (ratio = 1) levels (n = 5 for each group). (C) Effect of ketorolac (1 mg/kg, 3 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, and saline control; n = 5 for each group) on von Frey mechanical thresholds and (D) on the average paw luminance ratio. Baseline readouts were conducted before zymosan injection, the “pre” readouts were 4 hours after zymosan injection but before ketorolac administration, and the “post” were 1 hour after ketorolac administration. For the average paw luminance ratio, a significant reversal from saline levels was detected after 3 and 10 mg/kg ketorolac treatment. (E) Average paw luminance ratio and (F) total distance traveled (in pixel unit) and for 10-minute recordings, baseline readouts were conducted before zymosan injection, the “pre” readouts were 4 hours after zymosan injection but before diazepam administration, and the “post” were 30 minutes after diazepam. Data in panel (B), (C), (D), (E), and (F) presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance for panel (B) determined by the 2-tail unpaired Student t-test; for (C) and (D) by 2-way ANOVA repeated measures, followed by the Dunnett post hoc analysis; and for (E) and (F) by the paired Student t-test. UVB, ultraviolet radiation burn.