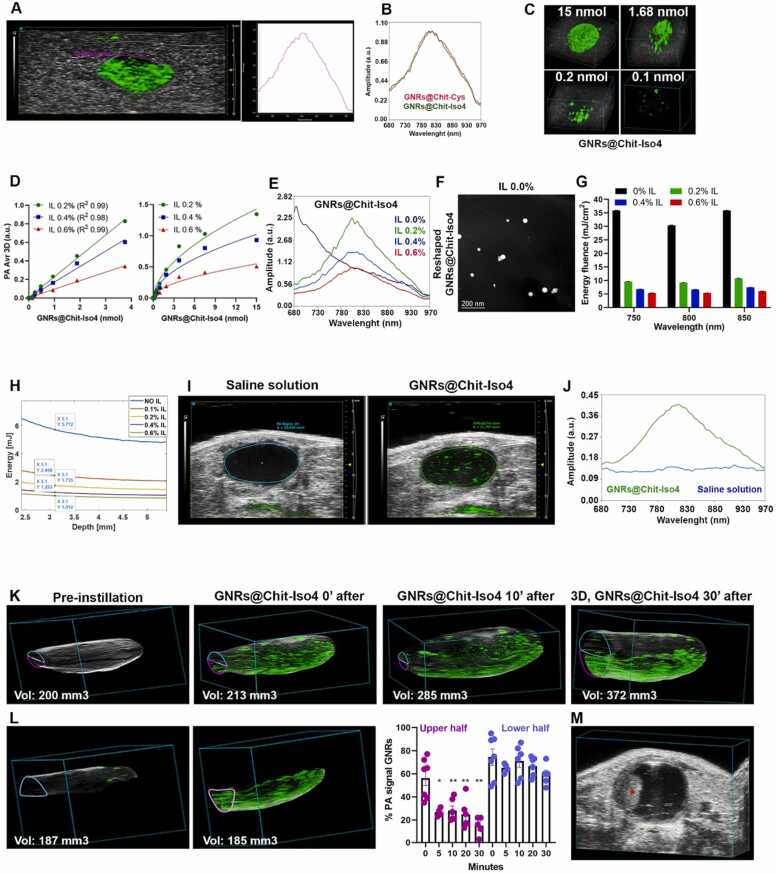
Fig. 5.
In vitroand in vivo PAI of GNRs@Chit-Iso4. A) PAI of agar drop containing GNR@Chit-Iso4 (15 nmol Au) and its associated PA spectrum using 0.6% Intralipid (IL) light-attenuators. The echogenic signal (gray) is generated by the slime in which the agar drop is embedded. The violet ROI delineates the PA signal of GNRs from which the PA spectrum was derived; the PA images were acquired and spectrally unmixed with VevoLab software to separate the contribution of the slime and GNRs (the green signal corresponds to the PA signal of GNRs). B) Normalized PA spectra of GNRs@Chit-Cys and GNRs@Chit-Iso4 (15 nmoli of Au) embedded in agar drop (one representative experiment of five). C) 3D distribution of the GNRs@Chit-Iso4 signal in agar drops acquired using the light attenuators made of 0.6% IL. D) Dose-response plot of the PA signal of GNRs@Chit-Iso4 in agar drop analyzed using light attenuators prepared with the indicated concentration of IL; linear dynamic range from 0 to 3.75 nmol Au, and trend towards plateau from 3.75 to 15 nmol Au (mean±SEM of duplicates are shown). E) Overlayed PA spectra of GNRs@Chit-Iso4 (3.75 nmol Au) acquired using light attenuators prepared with the indicated concentration of IL. F) TEM analysis of GNRs@Chit-Iso4 recovered from an agar drop after PA analysis conducted with a light attenuator prepared without IL. G) Energy fluence at 750, 800 and 850 nm, both in the absence and in the presence of light attenuators containing the indicated amounts of IL (mean±SEM of triplicates). H) Average energy distribution along the depth, from the Monte Carlo model of the simulated domain reported in the Supplementary Fig. S11. I) In vivo PAI of murine bladder after intravesical instillation of 100 μl of vehicles (saline solution) or GNRs@Chit-Iso4 (3 nmol Au), from representative frames taken in the middle of the bladder (one representative experiment of five); the green signal corresponds to the PA signal of GNRs after unmixing the PA signal of melanin, deoxy- and oxy-genated blood and GNRs. J) PA spectra of the saline solution and of GNRs@Chit-Iso4 (3 nmol Au) in the murine bladder. K) 3D distribution of the GNRs@Chit-Iso4 (3 nmol Au) PA signal in murine bladder imaged at the indicated time points (one representative experiment of five). L) 3D distribution of the GNRs@Chit-Iso4 PA signal in the upper and lower half of the murine bladder 30 min after instillation, followed by the quantification of the volume occupied by the PA signal (% PA signal of GNRs) in the upper and lower half of the bladder at the different time points (data shown as mean±SEM, each dot representative of one animal). * , * *; p value using 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test between upper and lower half of the bladder each time point). M) PAI of the murine bladder with a well-established tumor on the left side (red asterisk), showing a lack of PA signal after the intravesical instillation of GNRs@Chit-Iso4 (3 nmol Au) and two intravesical washing steps to remove the unbound GNRs; axial diameter of the bladder lumen = 3.7 mm. Vol: Volume.