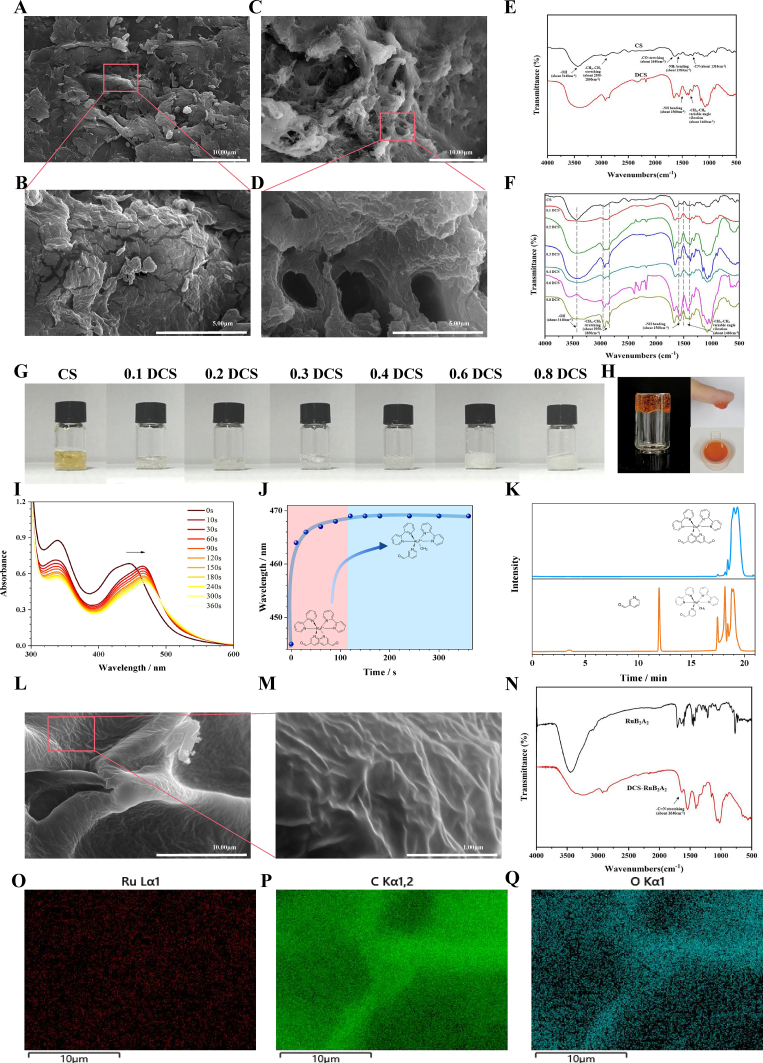
Fig. 2.
Performance characterization of DCS-Ru2BA2and exploration of the crosslinking mechanism. SEM images of CS (A, B) and DCS (C, D); scale bars 10 μm and 5 μm. (E) FTIR spectra of CS and DCS. (F) FTIR spectra of DCS with differing degrees of substitution. (G) Photographs of CS and DCS. (H) Photographs of DCS-RuB2A2. (I) UV–Vis spectral evolution of RuB2A2 (100 μmol L−1) in deionized water with increasing irradiation time (λex = 450 nm, 14 mW cm−2). (J) The wavelength corresponding to the UV absorption peak of RuB2A2 varies with illumination time. Pink represents the first stage and blue represents the second stage. (K) HPLC analysis of the photodegradation of crosslinkers under dark conditions (blue) and after illumination (orange). (L, M) SEM images of DCS-RuB2A2; scale bars 10 μm and 1 μm. (N) FTIR spectra of DCS-RuB2A2. (O-Q) Mapping images of C, O, and Ru elements of DCS-RuB2A2 in (L).