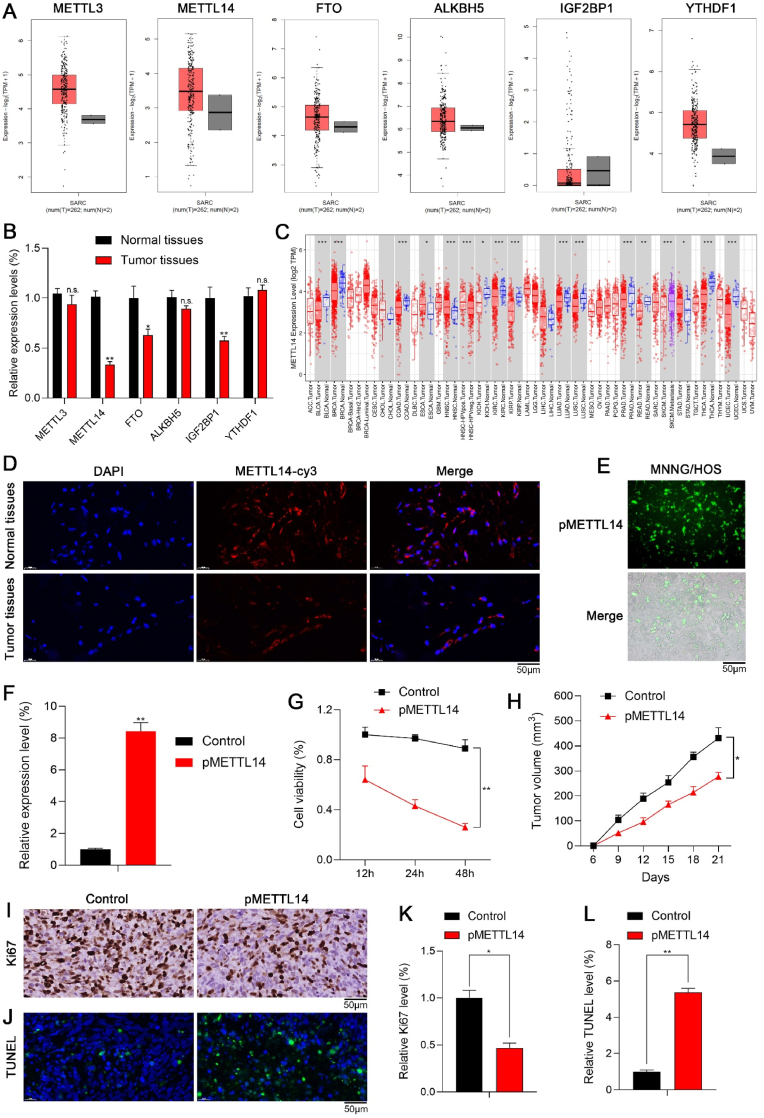
Fig. 1.
The anti-tumor effects of METTL14 in vitro and in vivo. (A) The expression levels of m6A regulators in sarcoma via GEPIA database. (B) qPCR showed the expression levels of m6A regulators in normal tissues and tumor tissues (n.s.: no significance; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05). (C) METTL14 was remarkably downregulated in most types of tumors via TIMER database (***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05). (D) IF staining of METTL14 in normal tissues and tumor tissues. (E) The fluorescence analysis indicated that pMETTL14 was successfully transfected in tumor cells. (F) qPCR showed that METTL14 was significantly upregulated in tumor cells of pMETTL14 group (**p < 0.01). (G) The CCK-8 assay indicated that the cell viability of tumor cells reduced significantly in pMETTL14 group (**p < 0.01). (H) The tumor growth pMETTL14 group was remarkably inhibited compared with control group (*p < 0.05). (I, K) The number of Ki67 positive cells via IHC staining in pMETTL14 group (scale bar: 50 μm; *p < 0.05). (J, L) The number of TUNEL positive cells in pMETTL14 group (scale bar: 50 μm; **p < 0.01).