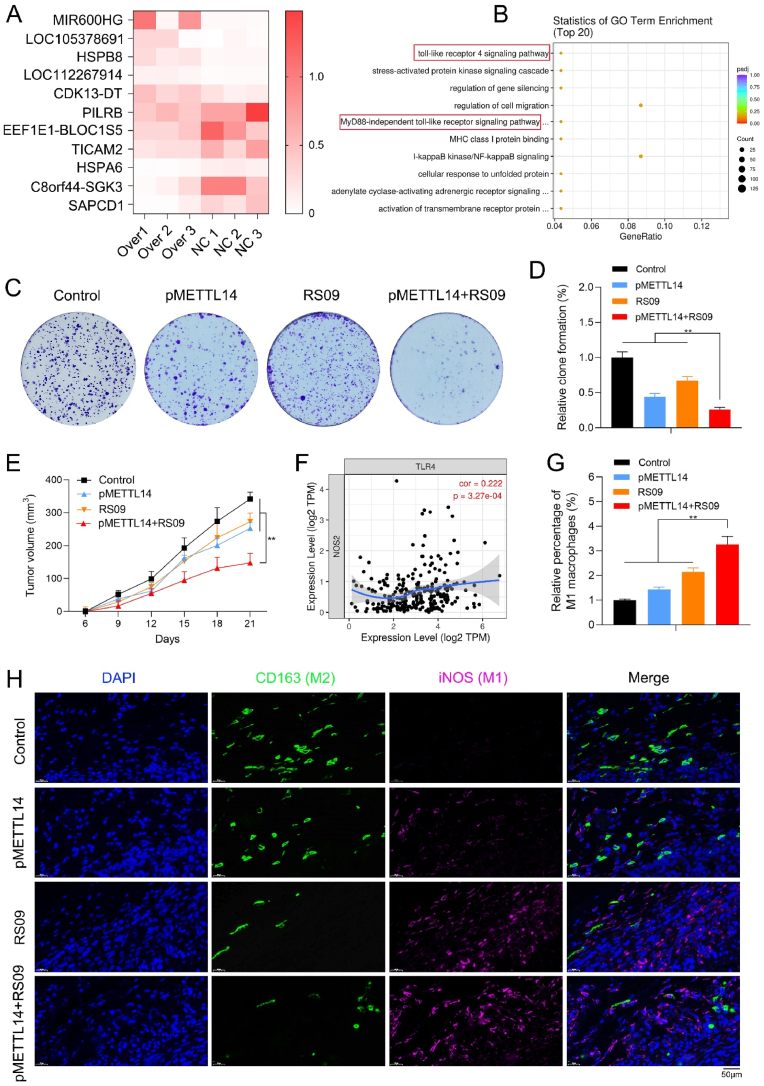
Fig. 3.
METTL14 combined with TLR4 agonist inhibit tumor and regulate macrophage polarization. (A) The cluster analysis of differentially expressed genes in pMETTL14 and normal groups of macrophages. (B) The GO enrichment analysis showed that METTL14 was remarkably correlated with the TLR4 signaling pathway of macrophages. (C, D) RS09 is one of the most common TLR4 agonists. The clone formation assay indicated that pMETTL14+RS09 group remarkably decreased tumor cell proliferation than other groups (**p < 0.01). (E) pMETTL14+RS09 significantly reduced the tumor volume when compared with other groups (**p < 0.01). (F) TLR4 showed a remarkably positive association with NOS2/iNOS (r = 0.222, p = 3.27e-04) of M1 type of macrophages via TIMER database. (G, H) The relative proportion of M1 (iNOS) and M2 macrophages (CD163) were observed in tumor tissues of control, pMETTL14, RS09, and pMETTL14+RS09 groups via IF staining (scale bar: 50 μm; **p < 0.01).