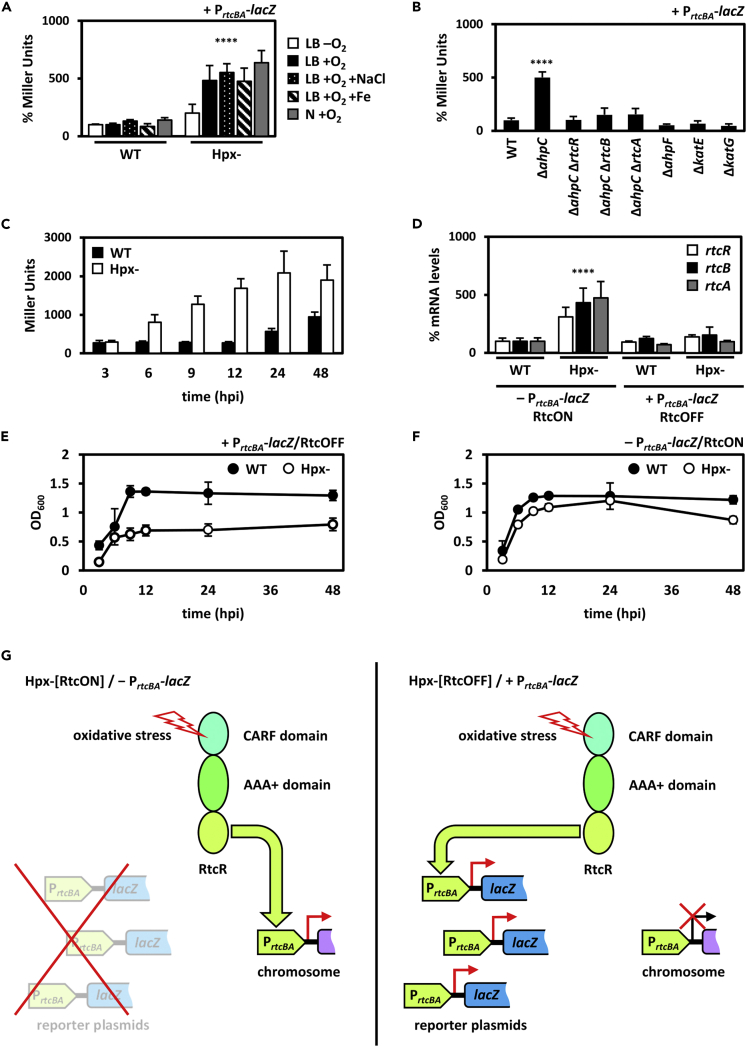
Figure 4.
The Rtc system is induced in the Hpx- strain
The transcriptional activation of the Rtc system in the Hpx- strain was assessed using β-galactosidase assays with cells harbouring a plasmid-encoded PrtcBA-lacZ reporter and RT-qPCR. In parallel, the growth of the Hpx- stain was monitored.
(A) The rtcBA promoter activity is induced in LB broth, LB broth supplemented with extra 5 g/L NaCl, LB broth supplemented with 50 μM Fe-citrate and nutrient broth, after 24 h under aerobic but not anaerobic conditions (N = 5).
(B) The rtcBA promoter activity is induced in the Hpx- strain because of gene deletion ΔahpC; RtcR, RtcB and RtcA are required for rtcBA promoter activity in the gene deletion mutants ΔahpC (N = 4).
(C and D) The rtcBA promoter activity is induced and (D) the rtc mRNA levels are increased, as shown by β-galactosidase reporter assays and RT-qPCR, respectively (N = 3).
(E) The presence of the PrtcBA-lacZ reporter plasmid leads to inhibited growth of the Hpx- compared to the wild-type (N = 3).
(F) In the absence of the PrtcBA-lacZ reporter plasmid, the inhibitory growth effect is not as evident (N = 3).
(G) Proposed model of the molecular events occurring in the Hpx- cells in the absence (left) and presence (right) of the PrtcBA-lacZ reporter plasmid: absence does not interfere expression of the chromosomal Rtc genes (left), leading to normal cell growth; presence interferes with expression of the chromosomal Rtc genes (right), leading to impaired cell growth. In panels (A, B, and D), β-galactosidase activity or mRNA levels of the wild-type strain is set as 100%. Data are shown as mean and error bars represent standard deviation from the mean. N represents total number of independent biological replicates, with 3 technical replicates each. ANOVA ∗∗∗∗ p-value < 0.0001.