Figure 5.
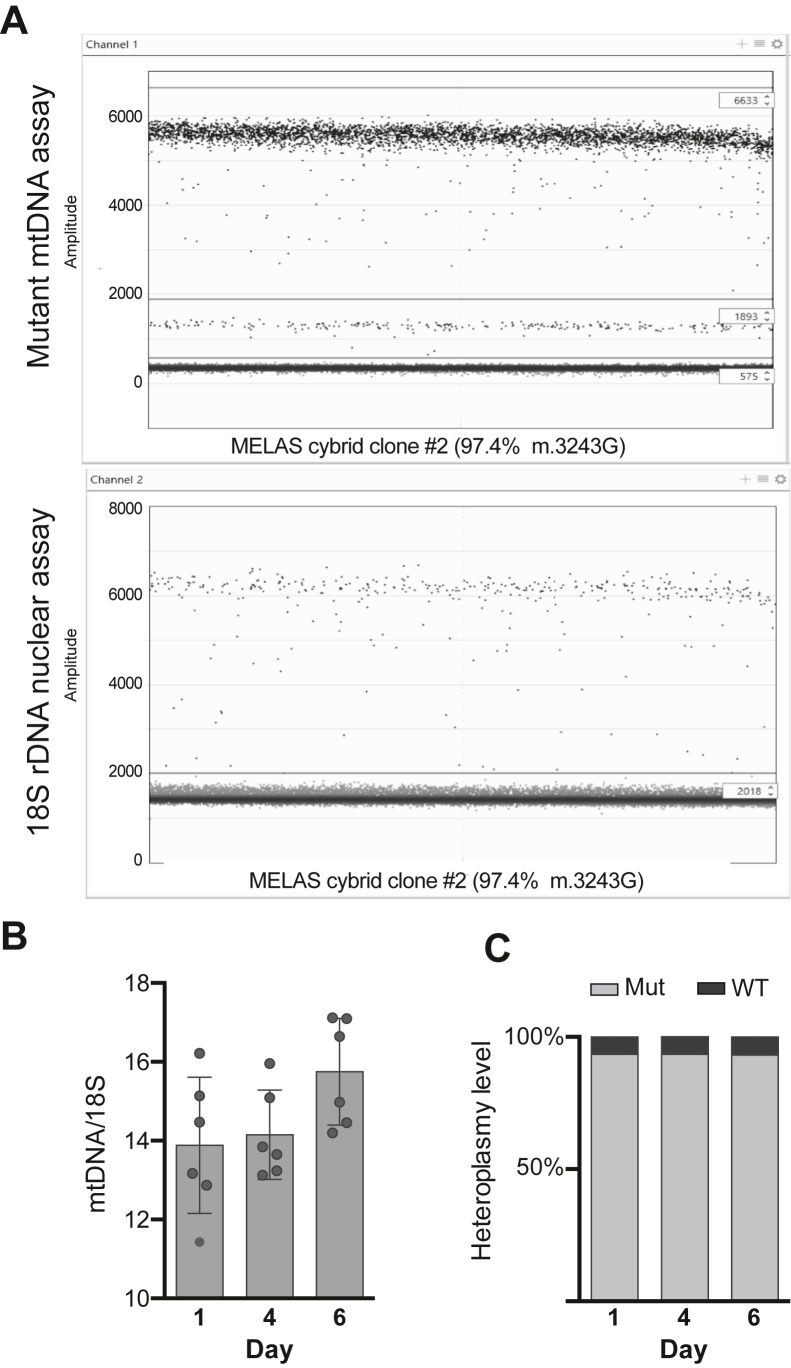
dPCR can be used to simultaneously quantify heteroplasmy and mtDNA copy number.A, sample duplex droplet dPCR plots for the mutant mtDNA assay (top) and 18S rDNA nuclear assay (bottom) using cellular DNA isolated from clone #2. 0.225 ng of DNA was used in the duplex. The mutant mtDNA assay used a FAM-labeled probe, while the 18S rDNA nuclear assay used a HEX-labeled probe. Horizontal lines are drawn to differentiate the distinct droplet populations in the mutant mtDNA assay (high-amplitude positive, low-amplitude positive, and negative) and 18S rDNA nuclear assay (positive and negative). B, quantification of mtDNA copy number using duplex dPCR. mtDNA copy number was calculated by dividing the concentration (copies/μl) of both positive droplet populations (high-amplitude + low-amplitude) in the mutant mtDNA assay by the concentration of positive droplets for the 18S rDNA nuclear assay. C, quantification of mtDNA heteroplasmy using the mutant mtDNA assay. The percentage of mutant mtDNA was quantified by dividing the concentration (copies/μl) of high-amplitude FAM-positive droplets by the concentration of total FAM-positive droplets (high-amplitude + low-amplitude). The percentage of WT mtDNA was quantified by dividing the concentration (copies/μl) of low-amplitude FAM-positive droplets by the concentration of total FAM-positive droplets (high-amplitude + low-amplitude). mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; dPCR, digital PCR.