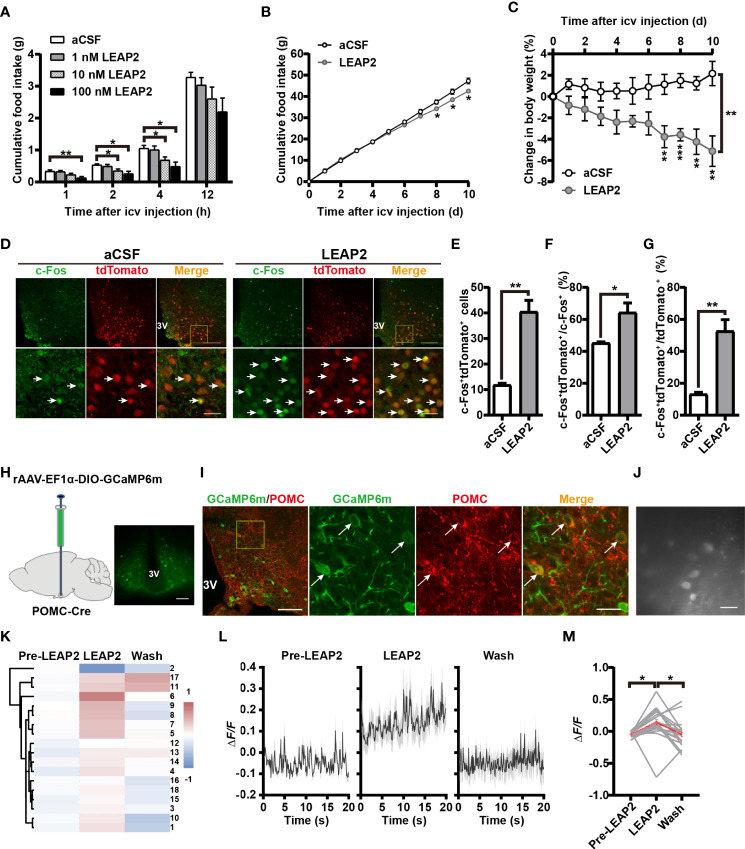
Figure 6.
LEAP2 decreases food intake and body weight and increases POMC neuronal activity in ARC. (A) Cumulative food intake during the dark cycle (12 h) of WT mice after an acute single i.c.v.-administered aCSF or LEAP2. n = 16–18/group, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test, F (3, 66) = 4.443, ** p = 0.0066< 0.01 for treatment, ** p = 0.0035< 0.01 for aCSF vs. 100 nM LEAP2, 1 h; * p = 0.0433< 0.05 for aCSF vs. 10 nM LEAP2, * p = 0.0150< 0.05 for aCSF vs. 100 nM LEAP2, 2 h; * p = 0.0489< 0.05 for aCSF vs. 10 nM LEAP2, * p = 0.0107< 0.05 for aCSF vs. 100 nM LEAP2, 4 h. (B, C) Cumulative food intake (B) and change in body weight (C) of WT mice during i.c.v. administration of aCSF or LEAP2 (10 nM) once each day for 10 days. n = 6/group, two-tailed Student’s t-test, t = 2.782, * p = 0.0194< 0.05, 8 days; t = 2.623, * p = 0.0255< 0.05, 9 days; t = 3.102, * p = 0.0112< 0.05, 10 days (B). Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test, F (1, 10) = 20.54, ** p = 0.0011< 0.01 for treatment (C). (D) Staining of c-Fos in the ARC of POMC-Cre;Rosa-tdTomato mice treated with a single i.c.v. injection of either aCSF or LEAP2 (10 nM). 3V, third ventricle. Arrows indicate c-Fos and tdTomato double-positive cells; 100 and 25 μm for the low- and high-magnification images, respectively. (E) The number of c-Fos+ and tdTomato+ cells in the ARC of mice administered aCSF or LEAP2. n = 6/group, two-tailed Student’s t-test, t = 6.408, ** p = 0.0012< 0.01. (F, G) The ratio of c-Fos and tdTomato double-positive cells to c-Fos-positive (F) and tdTomato-positive (G) cells. n = 6/group, two-tailed Student’s t-test, t = 3.230, * p = 0.0222< 0.05 (F); t = 5.495, ** p = 0.0023< 0.01 (G). (H) Bilateral injection of rAAV-EF1α-DIO-GCaMP6m into the ARC of POMC-Cre mice. Representative coronal section image showing GCaMP6m expression in the ARC of POMC-Cre mice. Scale bar, 200 μm. (I) Representative photographs showing the expression of POMC in GCaMP6m-positive neurons in the ARC of POMC-Cre mice. 3V, third ventricle. Arrows indicate GCaMP6m and POMC double-positive cells. 100 and 25 μm for the low and high-magnification images, respectively. (J) Example field of view from the microscope showing POMC cells. Scale bar, 50 μm. (K) Hierarchical cluster analysis of recorded neurons and heatmap of average ΔF/F of activity in the three stages, including pre-LEAP2, LEAP2 (100 nM) application, and washing out. (L) Response profiles (mean ± SEM) of POMC neuron clusters showing average activity traces aligned to pre-LEAP2, LEAP2 (100 nM) application, and washing out. (M) Average ΔF/F of calcium signals of all recorded POMC neurons in the three stages. Gray lines refer to individual neurons; the red line reflects the mean value. n = 18 neurons from four mice, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test, F (2, 51) = 5.257, ** p = 0.0084< 0.01; * p = 0.0271< 0.05 for Pre-LEAP2 vs. LEAP2, * p = 0.0385< 0.05 for LEAP2 vs. wash. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * p< 0.05; ** p< 0.01.