Figure 5.
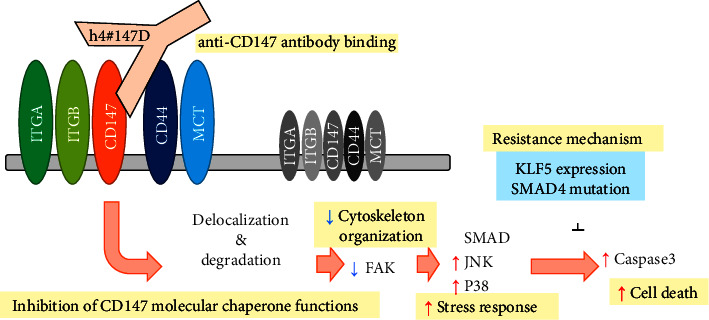
Graphical representation of a possible mechanism of action (MoA) for h4#147D anti-tumor efficacy. Administration of h4#147D leads to decreased cell surface expression of CD147 and its binding partners (such as integrins, CD44, and MCTs) via inhibition of CD147 molecular chaperone functions. Decreased or displaced CD44 and integrins may induce inhibition of FAK and cytoskeleton stress-mediated activation of stress-responsive signals such as SMAD, JNK, and P38MAPK. These activated stress-responsive signals lead to caspase-3 activation and cell death. Inhibitory mechanisms for the multiple stress-responsivesignal-induced cell death are possible mechanisms of resistance to the h4#147 mechanism of action.
