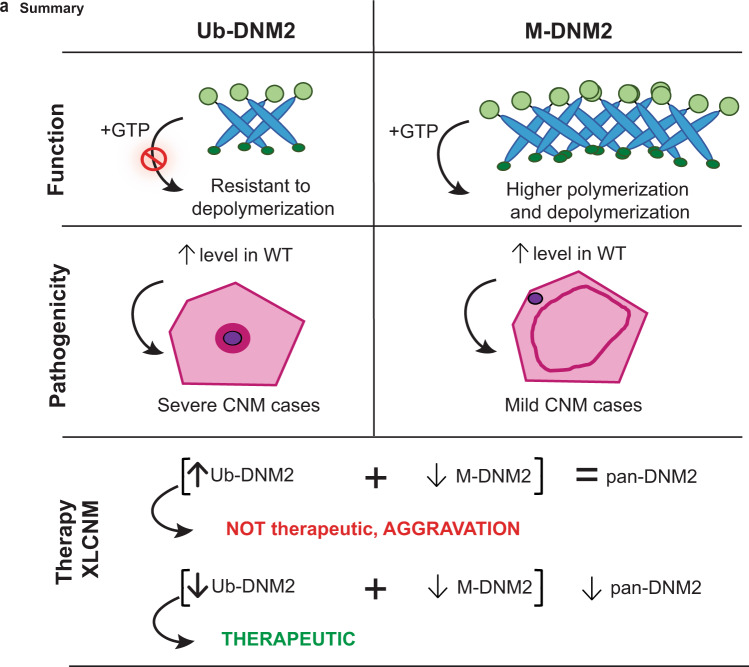
Fig. 9. Summary of the differential function and implications of DNM2 isoforms at pathophysiological and therapeutic levels.
Function: M-DNM2 was shown to form higher-order oligomer structures, while having faster GTP kinetics and higher sensitivity to GTP-induced depolymerization compared to Ub-DNM2 that was more resistant to depolymerization in presence of GTP. Pathogenicity: the differential molecular regulation of Ub-DNM2 and M-DNM2 underly that Ub-DNM2 exogenously expressed in mouse WT muscles triggered a severe CNM histology with centralized organelles, while expression of M-DNM2 led to a mild CNM phenotypes. Therapy: both isoforms have not an equivalent role in X-linked CNM (XLCNM) context as a splice switching strategy decreasing M-DNM2 while increasing Ub-DNM2 resulted in aggravation of the XLCNM phenotypes in mice, while maintaining an overall normal level of DNM2. Conversely, it was shown that decreasing the total level of pan-DNM2 resulted in the rescue of XLCNM mouse phenotypes38.