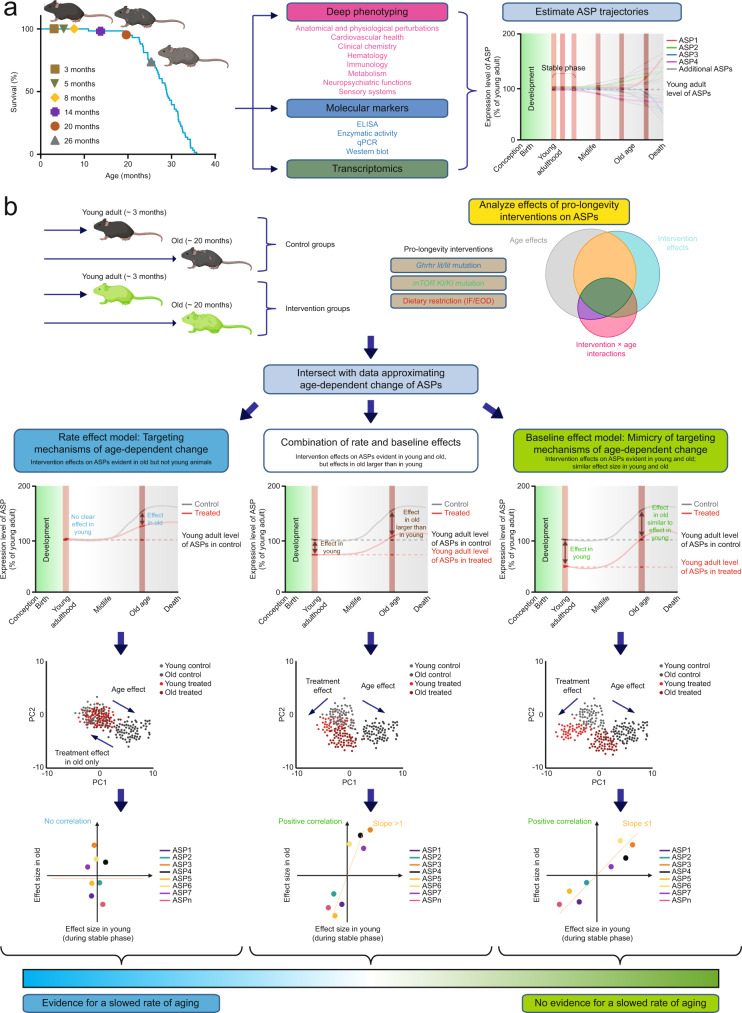
Fig. 1. To what extent can aging, measured as a multidimensional representation of age-dependent phenotypic change, be slowed in mice?
a To estimate aging trajectories for a wide range of age-sensitive phenotypes (ASPs), we examined phenotypes across the lifespan of C57BL/6J mice, including hundreds of phenotypes derived from multi-dimensional deep phenotyping, a range of molecular markers as well as transcriptomic profiles. b We assessed three important pro-longevity interventions for their effects on aging (putative anti-aging interventions; PAAIs). For each PAAI, we generated a young as well as an old cohort of experimental animals and controls, all of which were analyzed concurrently in one single study. For each phenotype in each of these studies, we determined age effects, intervention effects and intervention × age interactions based on the data derived from young and old control as well as experimental animals. These analyses revealed that some ASPs were influenced (countered or accentuated) by the PAAIs, others not. For ASPs countered by PAAIs, we considered the following scenarios: PAAIs could influence ASPs in a way consistent with slowing the rate of age-dependent change in ASPs (rate effect), via age-independent effects on ASPs (baseline effect) or via a combination of rate and baseline effects. To address what the age at first detectable change is for each ASP influenced by an intervention, we intersected data on ASPs from these intervention studies (see panel b) with data from our baseline study (see panel a). We compared effect sizes to examine for each ASP individually whether PAAI effects differed measurably between young and old mice. In addition, we used dimensionality reduction approaches as well as intraclass correlation analyses of intervention effect sizes in young and old animals to determine whether PAAIs overall act on ASPs primarily in a way consistent with slowing their rate of age-dependent change (left panels), via age-independent effects (right panels) or via a combination of rate and baseline effects (middle panels). For further details on our analytical approach, see Supplementary Fig. 1. Created with BioRender.com.