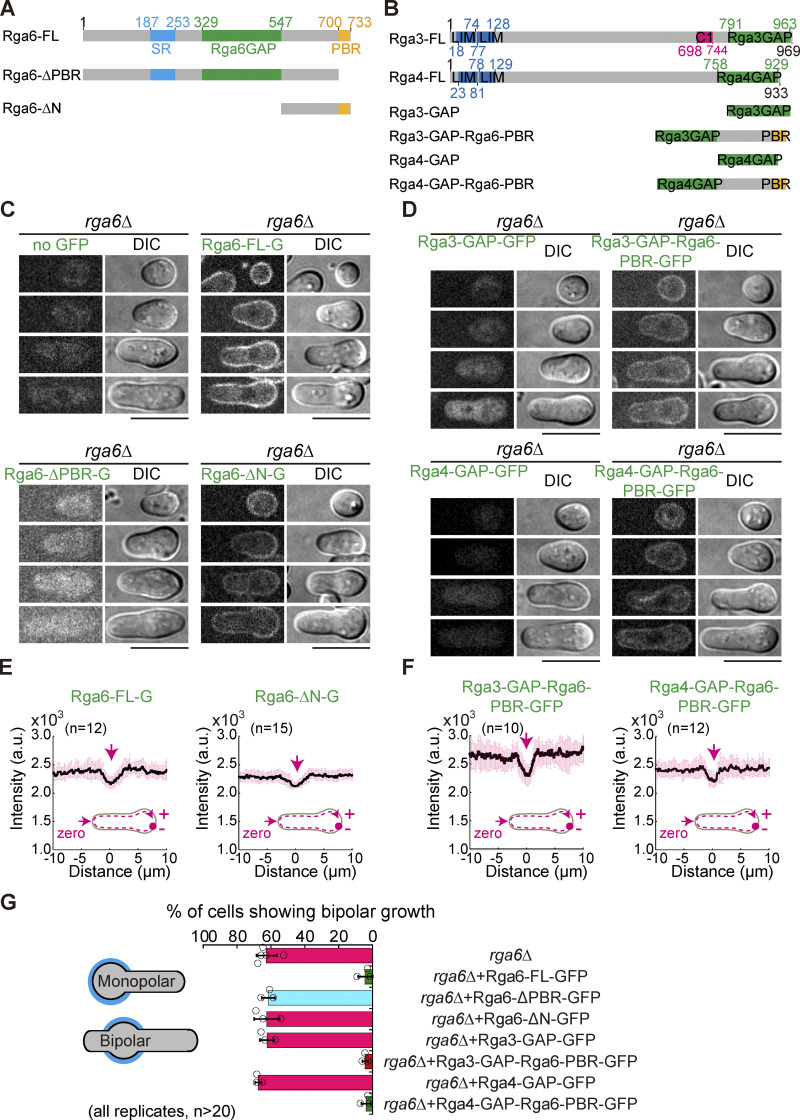
Figure 7.
Chimera proteins consisting of a GAP domain and the Rga6 PBR domain rescue the growth defect of spores caused by the absence of Rga6. (A and B) Domain structures of Rga6 (A), Rga3 (B), and Rga4 (B). Truncation and chimera mutants are also indicated. (C) Z-slice images of outgrowing rga6Δ spores expressing Rga6-FL-GFP (full-length Rga6), Rga6-ΔPBR-GFP (Rga6 lacking the C-terminal PBR domain), or Rga6-ΔN-GFP (Rga6 lacking the N-terminal region including the SR and GAP domains) from the ase1 promoter. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Z-slice images of outgrowing rga6Δ spores expressing Rga3-GAP-GFP (Rga3 GAP domain alone tagged with GFP), Rga3-GAP-Rga6-PBR-GFP (Rga3 GAP domain fused with the PBR domain derived from Rga6), Rga4-GAP-GFP (Rga4 GAP domain alone tagged with GFP), or Rga4-GAP-Rga6-PBR-GFP (Rga4 GAP domain fused with the PBR domain derived from Rga6) from the ase1 promoter. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E and F) Plots of average intensity (from the indicated number [n] of cells) of GFP signals along the cell contour as illustrated by the pink dashed line in the diagram. Zero indicates the geometric center of the growing end while “+” and “−” indicate the positive and negative distances on the x-axis, respectively. Thick lines and error bars represent the mean and SD, respectively. Black lines and error bars represent the mean and SD, respectively. (G) Quantification of the percentage of the indicated cells showing bipolar outgrowth during germination, determined by Calcofluor-white staining.