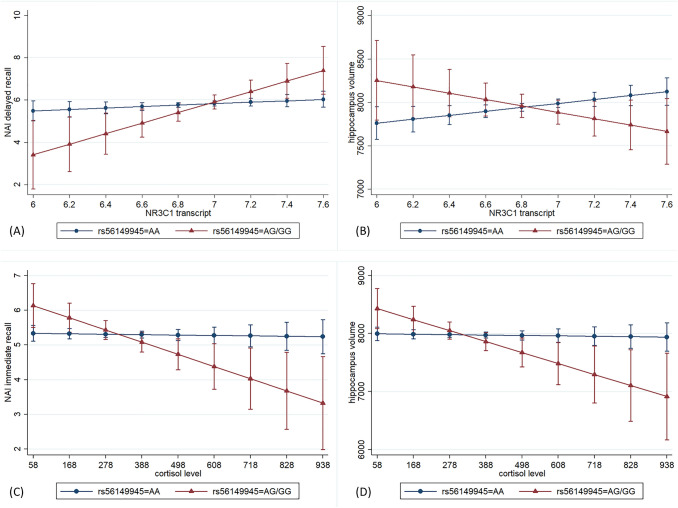
Fig. 3.
Significant interaction effects on verbal memory and hippocampal volume in the TREND subsample. Adjusted means with 95% confidence intervals. A Interaction between NR3C1 SNP rs56149945 and NR3C1 mRNA transcript on delayed recall corrected for time of blood sampling, RNA integrity number, RNA amplification batch, white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets, mean platelet volume, monocytes, lymphocytes, basophils, neutrophils, eosinophils, haematocrit, smoking status, BMI, educational level, current depressive symptoms, age, sex, and genetic PCs (n = 930). The negative effect of the G-allele of rs56149945 on delayed recall was reversed under the condition of a high expression level of NR3C1 transcript. B Interaction between NR3C1 SNP rs56149945 and NR3C1 mRNA transcript on hippocampal volume corrected for intracranial volume, time of blood sampling, RNA integrity number, RNA amplification batch, white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets, mean platelet volume, monocytes, lymphocytes, basophils, neutrophils, eosinophils, haematocrit, smoking status, BMI, educational level, current depressive symptoms, age, sex and genetic PCs (n = 784). The G-allele of rs56149945 was beneficial in case of a low NR3C1 mRNA transcript level, the AA-genotype in case of a high transcript level. C Interaction between NR3C1 SNP rs56149945 and cortisol level on immediate recall corrected for age, sex, smoking status, alcohol consumption, educational level, current depression score, fasting time, time of blood draw, waist-to-height ratio, HBA1C, white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets and genetic PCs (n = 824). The negative effect of the G-allele of rs56149945 was even stronger under a high cortisol level. An effect of the cortisol level for the AA genotype was not observed. D Interaction between NR3C1 SNP rs56149945 and cortisol level on hippocampal volume corrected for intracranial volume, age, sex, smoking status, alcohol consumption, educational level, depressive symptoms, fasting time, time of blood draw, waist-to-height ratio, HBA1C, white blood cells, red blood cells, platelets and genetic PCs (n = 699). The effects were similar to those on verbal memory [compare (C)]