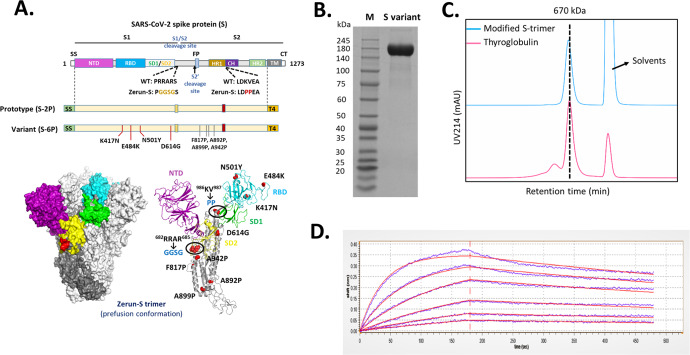
Fig. 1. Molecular design and characterization of variant S-trimer.
A Domain architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein. SS signal sequence, NTD N-terminal domain, RBD receptor-binding domain, SD1 subdomain 1, SD2 subdomain 2, S1/S2 S1/S2 protease cleavage site, S2' S2' protease cleavage site, FP fusion peptide, HR1 heptad repeat 1, CH central helix, CD connector domain, HR2 heptad repeat 2, TM transmembrane domain, CT cytoplasmic tail. Prototype S-trimer (S-2P) contains two consecutive proline substitutions at residues 986 and 987, a “GGSG” substitution at the furin cleavage site, and a C-terminal T4 fibritin trimerization motif. Variant S-trimer (S-6P) contains additional four beneficial proline substitutions (F817P, A892P, A899P, and A942P), and four hot spot residues (K417N, E484K, N501Y, and D614G). The structure model of S-trimer was generated by the SWISS-MODEL using homology modelling techniques (http://swissmodel.expasy.org/), and the 3D structure figures were prepared using PyMOL (www.pymol.org). B SDS-PAGE analysis of purified variant S-trimer. Molecular weight standards are indicated at the left in kDa. C Size-Exclusion HPLC chromatogram of purified variant S-trimer (shown as cyan line) and a 670 kDa molecular weight standard (shown as purple line). D Binding profiles of variant S-trimer to human ACE2 measured by BLI in GatorPrime. The data are shown as blue lines, and the best fit of the data to a 1:1 binding model is shown in red.