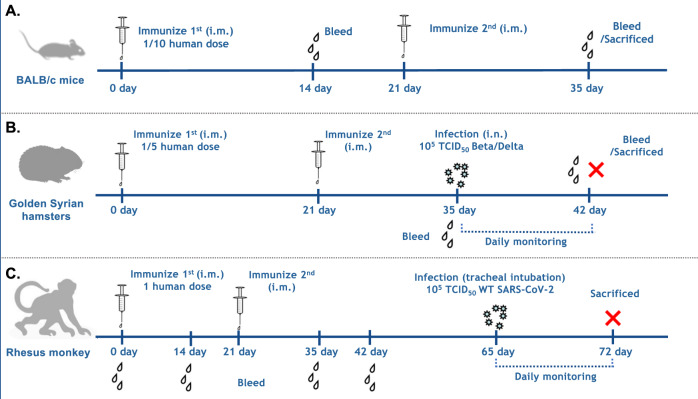
Fig. 2. Experimental schedule.
A BALB/c mice were immunized twice intramuscularly at Day 0 and Day 21. On Day 35, blood was collected to perform serological assays (SAs) (N = 10). On Day 35, 5 mice from each groups were sacrificed to conduct intracellular staining (ICS) assay and ELISPOT (N = 5). B Hamsters were immunized intramuscularly at Day 0 and Day 21 (N = 6). Blood was collected at Day 35 from each group to detect antibody responses. On Day 42, all hamsters were challenged intranasally with 105 TCID50 of Beta strain or Delta strain. On Day 49, a subset of hamsters in each group was euthanized for detecting viral loads of lungs and nasal turbinates by qRT-PCR and evaluating lung histopathology by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. C Rhesus macaques were immunized twice intramuscularly at Day 0 and Day 21 (N = 6). Blood was collected at Day 0, Day 14, Day 28 and Day 35 to perform serological assays (SAs). In addition, PBMCs were isolated at Day 35 to detect cellular immune responses by intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) and ELISPOT. On day 65, all the rhesus macaques were challenged with 1 × 105 TCID50 SARS-CoV-2 by tracheal intubation. After challenged, the body weight, temperature and viral load of throat, nasal, anal and blood swabs were daily monitored. On day 72, rhesus macaques were euthanized for detecting viral loads of lungs and trachea-bronchus by qRT-PCR and evaluating lung histopathology by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining.