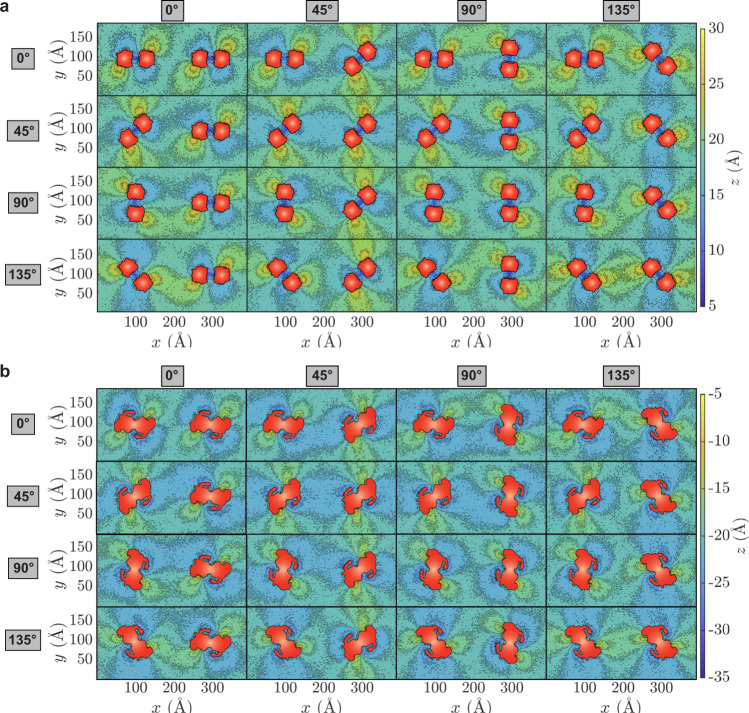
Fig. 3. Constructive or destructive interference of deformation patterns induced by prestin’s different orientations.
Heatmaps of phospholipid height in the outer (a) and inner (b) leaflets are calculated using the procedure described in Fig. 2. The prestin dimers are placed at (x, y) = (100, 100) Å and (300, 100) Å, respectively. The orientation of Dimer I (angle with respect to the x axis) is specified on the left, and for Dimer II on the top of each panel. Given the symmetry relation between prestin’s protomers, four angles (0°, 45°, 90°, and 135°) for each prestin dimer are sufficient to cover all possible orientations (at 45° intervals), resulting in 16 different combinations of two dimers. The protein cross-sectional area in each leaflet is drawn in red.