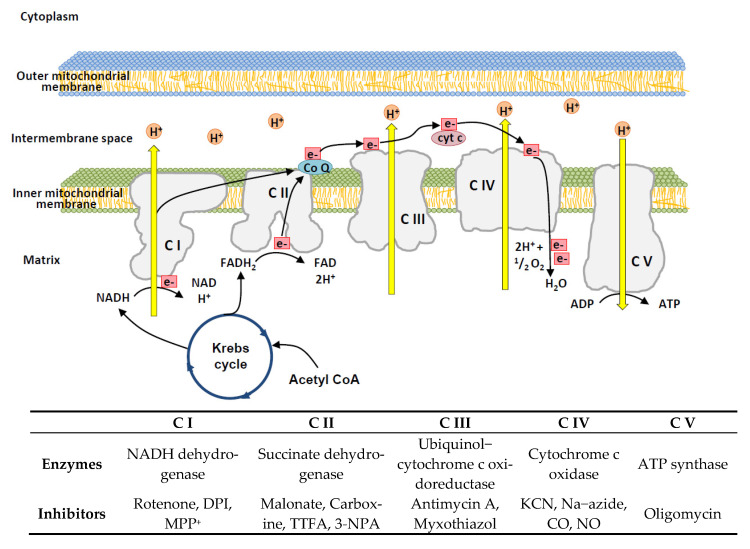
Figure 1.
Schematic model of the oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) process and relative inhibitors. In the electron transport chain, the reduced substrates NADH and FADH2 are oxidized by NADH−ubiquinone oxidoreductase and succinate−CoQ reductase, respectively. Finally, cytochrome c oxidase reduces molecular oxygen to water using electrons from reduced cytochrome c. The Krebs cycle is one of the main suppliers of redox equivalents. OXPHOS inhibitors are shown in the lower box. 3-NPA, 3-nitropropionic acid; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; C I, Complex I; C II, Complex II; C III, Complex III; C IV, Complex IV; C V, Complex V; CO, carbon monoxide; CYTC, cytochrome c; CoQ, coenzyme Q10; DPI, diphenyleneiodonium; KCN, potassium cyanide; MPP, 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium; Na−azide, sodium azide; NADH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NO, nitric oxide; TTFA, thenoyltrifluoroacetone.