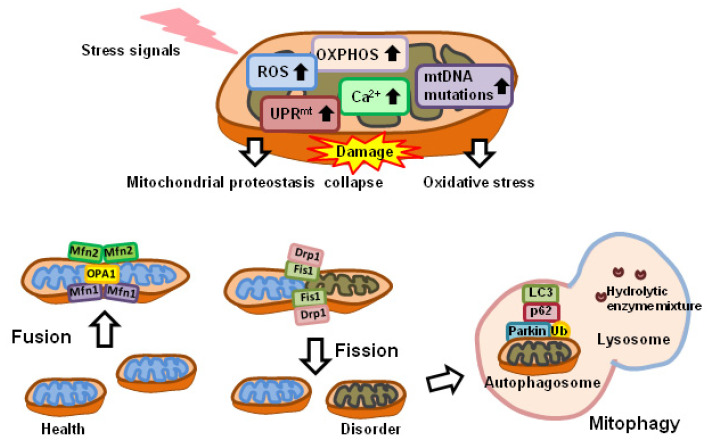
Figure 2.
Mitochondrial dysfunction, dynamics, and mitophagy. Mitochondrial dysfunction is accompanied by increased ROS production, UPRmt, Ca2+, and mtDNA mutations, as well as altered cellular respiration and altered metabolism. Mitochondrial fission is the splitting of mitochondria into two smaller mitochondria. DRP1 is recruited by FIS1 anchored on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Mitochondrial fusion refers to the merging of two mitochondria into one. MFN1 and MFN2 mediate mitochondrial outer membrane fusion, and OPA1 mediates mitochondrial inner membrane fusion. After mitochondrial depolarization, PINK1 accumulates on the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) and recruits Parkin to the mitochondrial surface. Parkin ubiquitinates various OMM proteins. Polyubiquitinated proteins can be recognized by adaptor molecules, such as p62. These proteins interact with lipidated LC3 through the LC3-interacting region (LIR) motif, promoting the autophagosome encapsulation of damaged mitochondria. LC3, light chain 3; MFN1, mitofusin1; MFN2, mitofusin2; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; OPA1, optic neurotrophin 1; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; p62, p62/Sequestosome 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Ub, ubiquitin; UPRmt mitochondrial unfolded protein response.