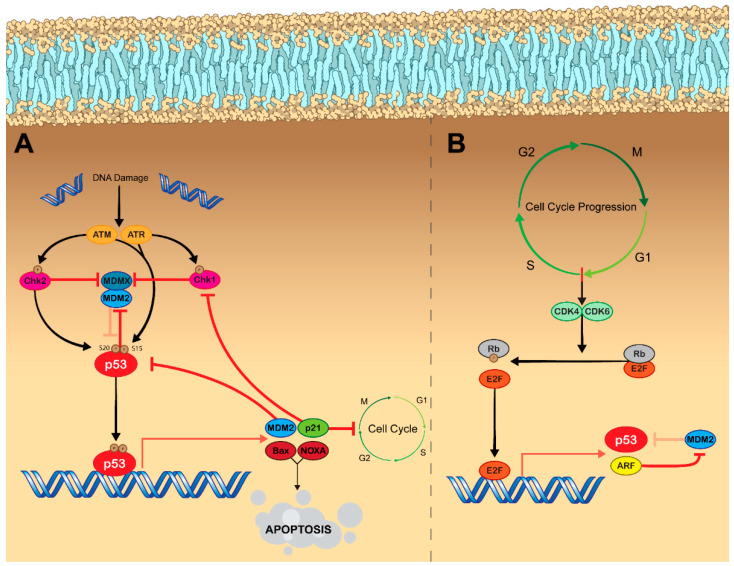
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of p53 activation. (A) DNA damage results in p53 activation via engaging the DDR pathway. Following detection of single stranded or double stranded DNA breaks, the kinases ATM and ATR become activated. Both ATM and ATR phosphorylate p53 at Ser15. ATM also phosphorylates Chk2, which phosphorylates p53 at Ser20, while ATR phosphorylates Chk1. Phosphorylation of p53 at Ser15 and Ser20 causes it to be released from its negative regulator, MDM2. Additionally, Chk2 and Chk1 both inhibit MDMX, which functions to enhance the E3 ligase activity of MDM2 and inhibit p53. With p53 now released from MDM2, it functions as a transcription factor resulting in the expression of various tumor suppressive genes. For example, Bax and NOXA are proapoptotic proteins, while p21 functions to inhibit cell cycle progression. p53 also plays a role in regulating its own activity by facilitating the expression of more MDM2, while p21 acts to inhibit further DDR signaling by blocking the activity of Chk1. (B) Cell cycle progression also leads to increased activity of p53. As cells prepare to enter the S phase of the cell cycle, the kinases CDK4 and CDK6 become activated. CDK4/CDK6 phosphorylate the cell cycle inhibitor protein Rb, which causes it to dissociate from E2F. E2F is now free from inhibition and functions as a transcription factor resulting in the expression of genes that facilitate cell cycle progression. E2F also facilitates the expression of p53 as well as ARF, which functions as an MDM2 inhibitor—therefore engaging p53 signaling. E2F can also facilitate nuclear accumulation of p53 by blocking its nuclear export signal. Legend: Arrows represent activation pathways, hammers represent inhibition, faded hammers represent inhibitory pathways that are being repressed by the signal pathway. Abbreviations: ATM, ataxia–telangiectasia mutated kinase; ATR, ataxia-telangiectasia, and Rad3-related kinase; Chk1/Chk2, checkpoint kinases 1&2; MDM2, mouse double minute 2 homolog; MDMX mouse double minute X; CDK4/CDK6, cyclin-dependent kinases 4&6; Rb, retinoblastoma protein; E2F, E2 factor; ARF, alternative reading frame (p14).