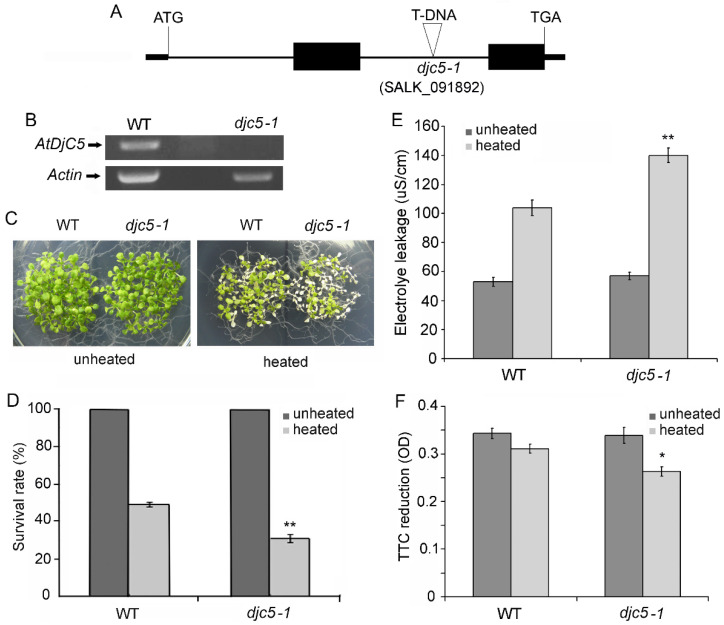
Figure 1.
AtDjC5 knockout decreased the basal thermotolerance. WT, wild-type plants; djc5-1, a T-DNA insertion mutant line for the AtDjC5 gene; unheated, under normal conditions; heated, treated at 44 °C for 90 min. (A) Intron/exon organization of the AtDjC5 coding region and T-DNA insertion location. Solid boxes, exons; lines, introns; triangles, T-DNA insertion position. (B) RT–PCR analysis of the AtDjC5 full transcript in WT and djc5-1 plants. (C) Comparison of WT and djc5-1 seedling viability. (D) Survival rates of WT and atdj5c-1 seedlings. Each value is the mean ± SD of ten biological replicates. (E) Electrolyte leakage assay for the WT and djc5-1 leaves. The data are the means ± SDs of three independent experiments. (F) 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) reduction activity of roots for WT and djc5-1. The data are the means ± SDs of four biological replicates, with a total of 30 roots per sample. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the WT of the same treatment (t test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01).