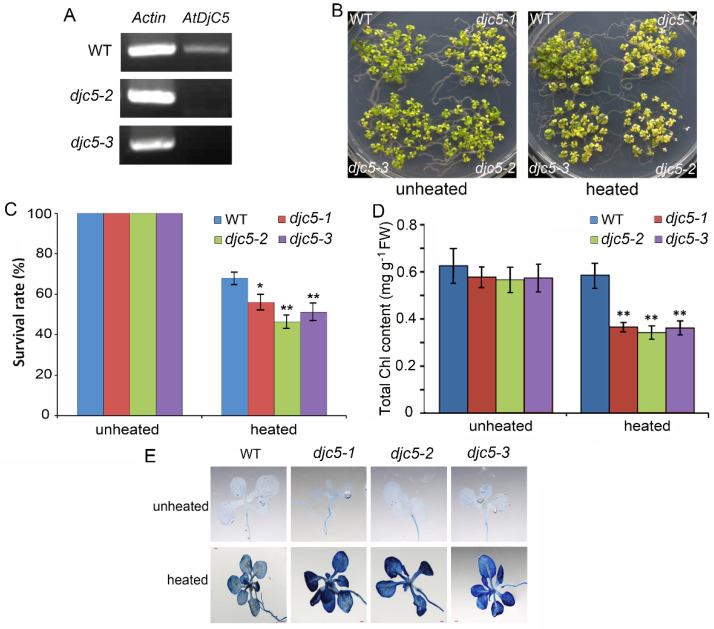
Figure 2.
AtDjC5 knockout decreased the acquired thermotolerance. WT, wild-type plants; djc5-1, a T-DNA insertion mutant line for AtDjC5 gene; djc5-2 and djc5-3, two AtDjC5 mutant lines by artificial microRNA; unheated, under normal conditions; heated, treated at 37 °C for 30 min, then 22 °C for 120 min, followed by 45 °C for 120 min. (A) RT–PCR analysis of the AtDjC5 full transcript in WT, djc5-2, and djc5-3 plants. (B) Comparison of the WT and AtDjC5 mutant seedling viability. (C) Survival rates of WT and AtDjC5 mutant seedlings. Each value is the mean ± SD of ten biological replicates. (D) Total chlorophyll contents in WT, djc5-1, djc5-2, and djc5-3 leaves. The data are the means ± SDs of four biological replicates. (E) Analysis of cell death in the WT and three AtDjC5 mutant lines before and after heat stress by trypan blue staining. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the WT of the same treatment (t test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01).