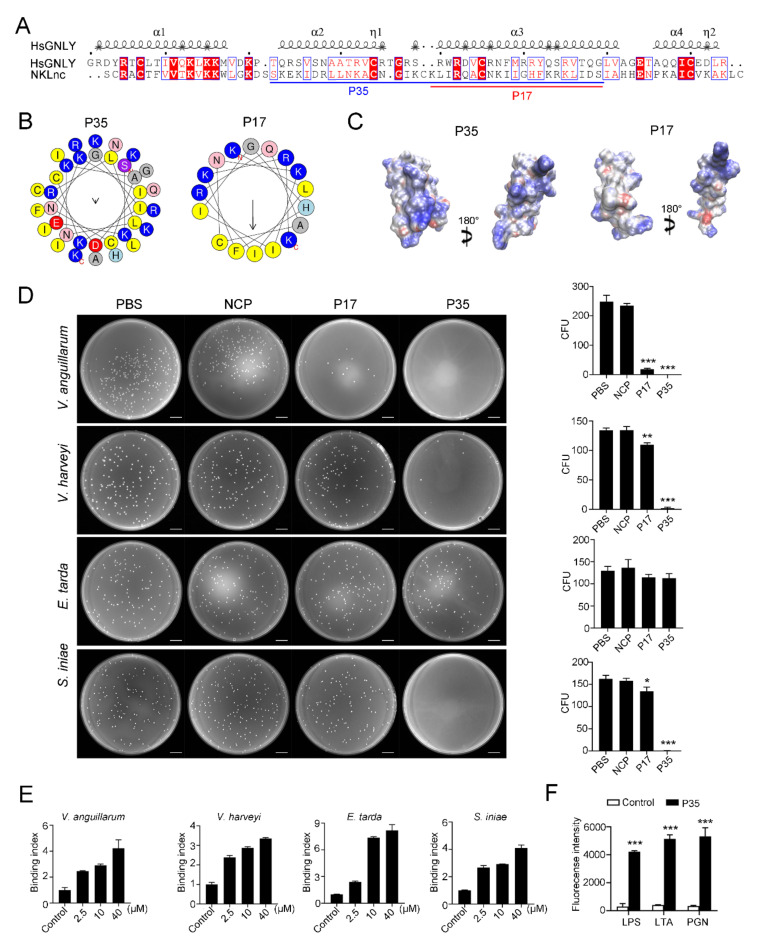
Figure 4.
NKLnc peptide structure and antimicrobial activity. (A) Secondary-structure-based alignment of the SapB domain sequences in human granulysin (HsGNLY) and NKLnc. The conserved amino acid residues are highlighted in red (100% identical) or boxed. The secondary structure is indicated on the top of the aligned sequence. P35 and P17 are underlined in blue and red, respectively. (B,C) The helical wheels (B) and electrostatic surface potentials (C) of P35 and P17. In (B), the residues that are positively charged, negatively charged, and hydrophobic are in blue, red, and yellow, respectively. In (C), the positive- and negative-charged regions are in blue and red, respectively. (D) Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio harveyi, Edwardsiella tarda, and Streptococcus iniae were incubated with P17, P35, the negative control peptide (NCP), or PBS for 2 h. Bacterial survival was determined by plate count. The bacterial numbers (shown as colony forming unit, CFU) are shown on the right panels. Scale bar, 1 cm. (E) Bacteria binding to different doses of P35 or control peptide (40 μM) was determined by ELISA. (F) LPS, LTA, and PGN binding to P35 or control peptide were determined by ELISA. For panels (D–F), values are the means of triplicate experiments and shown as means ± S.D. *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05.