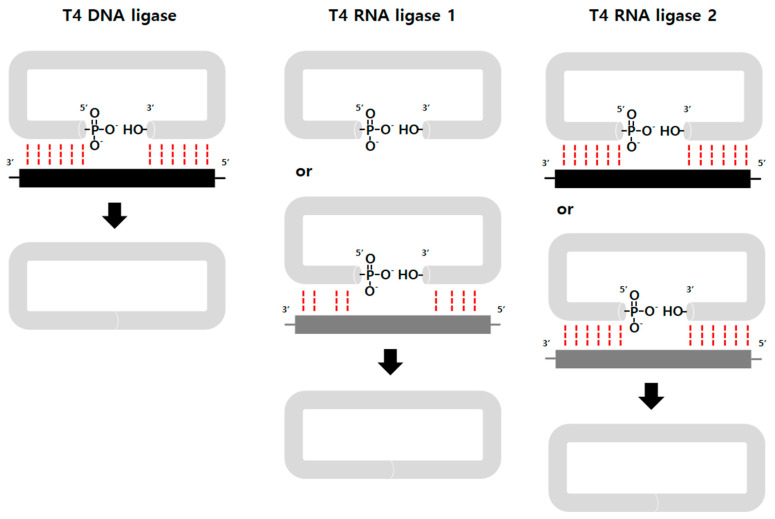
Figure 3.
Enzyme-based methods. T4 DNA ligase requires ATP as a cofactor and catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between a 5′-phosphate and a 3′-hydroxyl group, only in cases of perfect complementarity (red dotted line) between the two strands (RNA in gray, DNA splint in black) at the ligation junction [32]. T4 RNA ligase 1 accepts DNA and RNA fragments as substrates and works on single-stranded substrates with lower reaction specificity [33]. RNA splint (dark gray) or intrinsic secondary structure leaving 2~3 nucleotides unpaired increases efficiency [26,34]. T4 RNA ligase 2 ligates the RNA acceptor strand (3′-OH) with RNA or the DNA donor strand (5′-phosphate) [35]. An RNA or DNA splint can be used to bring the 5′ and 3′ ends together.