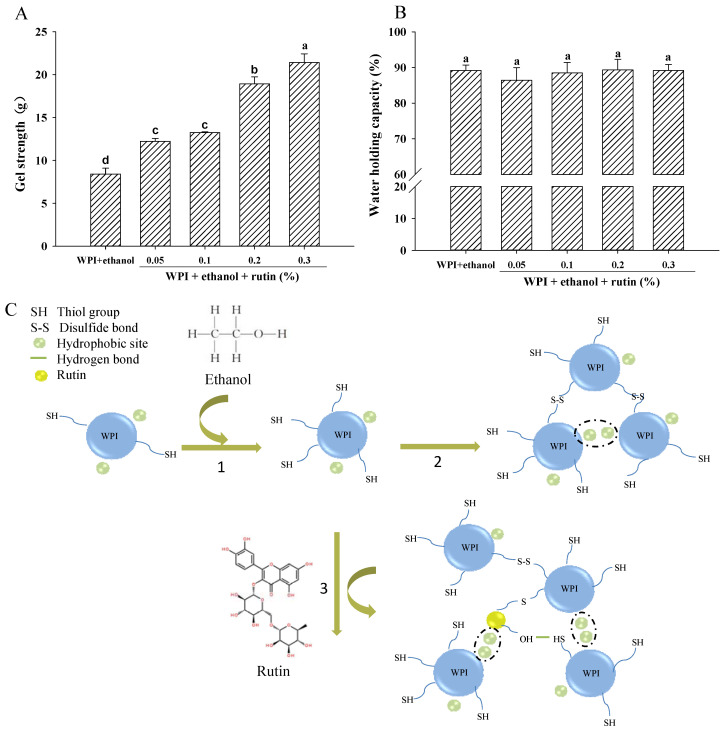
Figure 6.
The effects of ethanol (15% v/v) and different levels of rutin (0.05%, 0.1%, 0.2% and 0.3% w/v) on the gel strength (A), water-holding capacity (B) of WPI-based gels and the proposed interactions of WPIs induced by ethanol and rutin (C). Means with different letters (a–d) differ significantly (p < 0.05). 1. Unfolding of the WPI structure and exposure of the thiol groups and hydrophobic sites of WPI; 2. Cross-linking of WPI via hydrophobic interactions and disulfide bonds induced by ethanol; 3. Rutin might act as a cross-linker via hydrophobic interactions and formation of thiol–quinone adducts and hydrogen bonds with WPI.