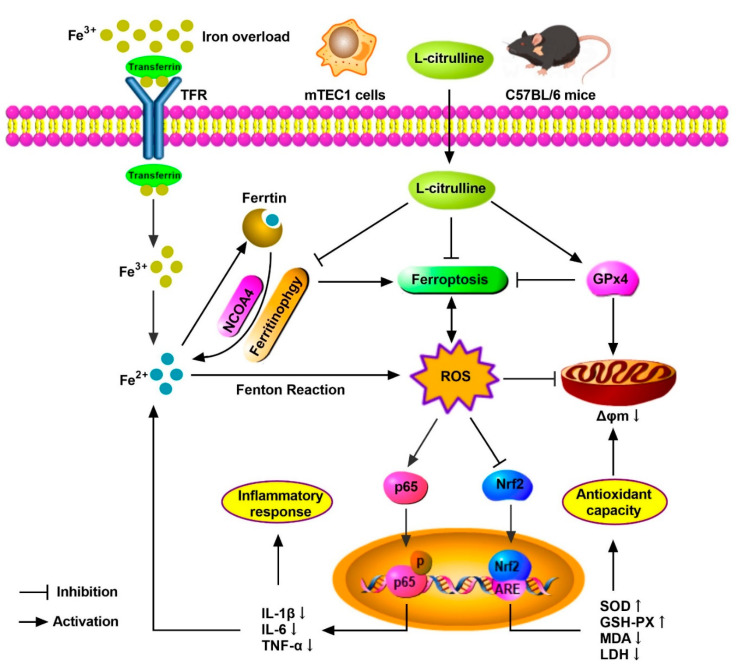
Figure 10.
The schematic illustration of underlying mechanism of L-cit alleviating oxidative damage and immune dysfunction. As a result, L-cit alleviates thymus histological damage, reduces the iron deposition, improves antioxidative capacity, and restrains NF-κB pathway in the mouse thymus and mTEC1 cells. NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy and ferroptosis were attenuated. L-cit might target ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis to decrease iron deposition and exert antioxidation and anti-inflammation response, which could be a therapeutic strategy against iron overload-induced oxidative damage and immune dysfunction.