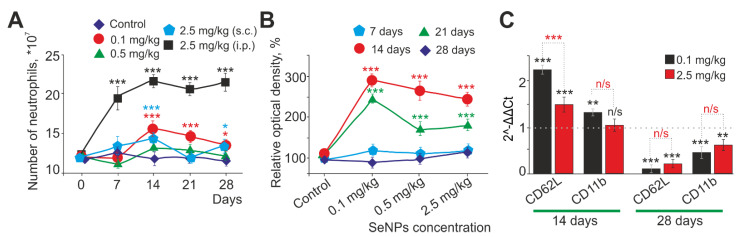
Figure 1.
Effect of injection of various concentrations of SeNPs into mice on the neutrophil number and adhesion. (А)—Dose- and time-dependent increase in the number of neutrophils isolated from mice peritoneal cavities after zymosan injection. The curves show the counts of neutrophil migration induced by zymosan (5 mg/mL) at 5 h after the daily intraperitoneal injection of SeNPs or saline (control) on days 7, 14, 21, and 28. Abbreviations: 2.5 mg/kg (s.c.)—subcutaneous injections of SeNPs and 2.5 mg/kg (i.p.) intraperitoneal injections of SeNPs. The data are the mean values ± SEM of seven mice. * p < 0.01 compared with respective control group. Peritoneal evoked neutrophils of male mice of outbreed strain BALB/c were used in the experiments. Neutrophils comprised nearly 98% of the total number of cells, as determined by acridine orange staining. (B)—Dose- and time-dependent modification of neutrophil adhesion on days 7, 14, 21, and 28 after daily injection of SeNPs or saline (control). Concentration-dependent effects of SeNPs (0.1 mg Se/kg, 0.5 mg Se/kg, 2.5 mg Se/kg) on mouse neutrophil adhesion: сurves shown are blue—on day 7, red—on day 14, green—on day 21, and dark blue—on day 28 of administration of SeNPs, respectively. Adhesion was determined by spectrophotometric analysis at 492 nm and then OD492 in the neutrophils from experimental groups with administration of SeNPs normalized to the same parameter measured in control group. Data presented are the mean ± SEM (n = 7). Statistical analyses of experimental groups vs. control were performed with paired t-test. Significance between group means: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001. Values not marked with an asterisk are invalid. (C)—Effect of SeNP injection in vivo on expression of neutrophil adhesion molecules CD11b and CD62L. Relative mRNA expression of genes encoding of CD11b and CD62L in neutrophils on days 14 and 28 after daily injection of 0.1 mg Se/kg (black bars) and 2.5 mg Se/kg (red bars) SeNPs. Dashed line—level of gene expression in controls (mice with administration of saline). GAPDH was used as housekeeping gene. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of five independent experiments. Statistical analysis of experimental groups versus control was performed with paired t-test and is marked with black asterisks. Significance between experimental groups is marked with red asterisks: *** p < 0.001 and ** p < 0.01; n/s—no significance.