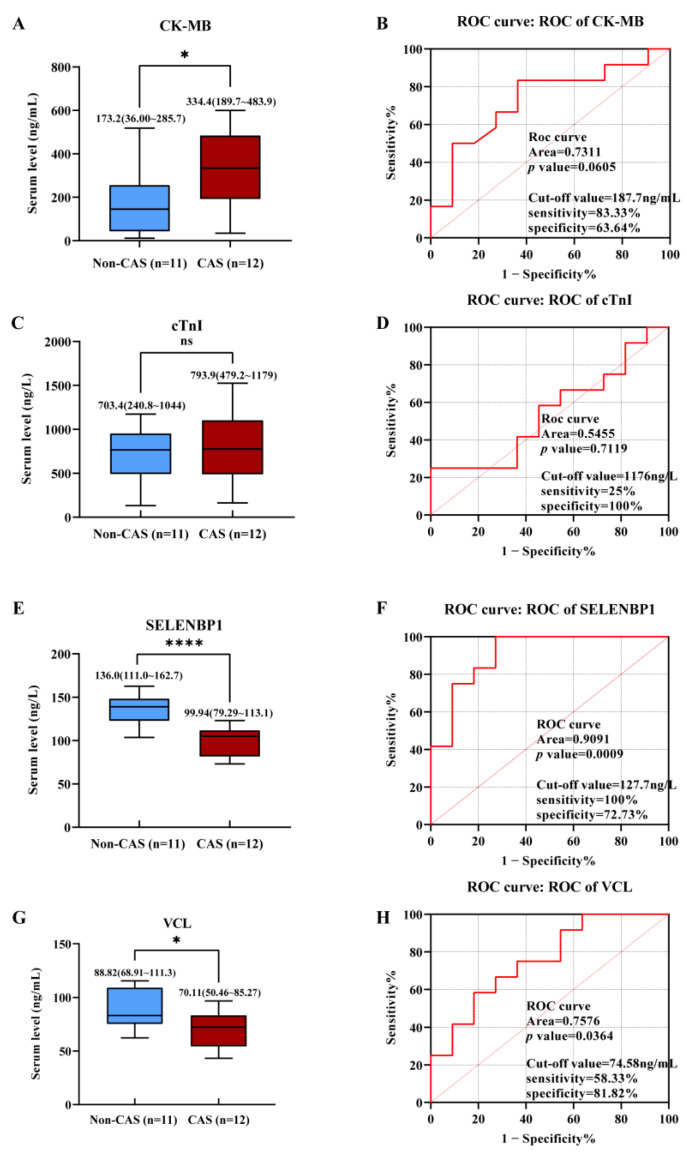
Figure 6.
Serum SELENBP1 or VCL alone could be biomarkers for forensic diagnosis of CAS-induced sudden death. (A) Serum CK-MB levels in non-cardiac death (non-CAS) and CAS-induced sudden deaths. (B) ROC analysis of serum CK-MB for the diagnosis of CAS-induced sudden death. (C) Serum cTnI levels in non-cardiac death (non-CAS) and CAS-induced sudden deaths. (D) ROC analysis of serum cTnI for the diagnosis of CAS-induced sudden death. (E) Serum SELENBP1 levels in non-cardiac death (non-CAS) and CAS-induced sudden deaths. (F) ROC analysis of serum SELENBP1 for the diagnosis of CAS-induced sudden death. (G) Serum VCL levels in non-cardiac death (non-CAS) and CAS-induced sudden deaths. (H) ROC analysis of serum VCL for the diagnosis of CAS-induced sudden death. ns—no significant. *, p < 0.05; ****, p < 0.0001 as indicated.