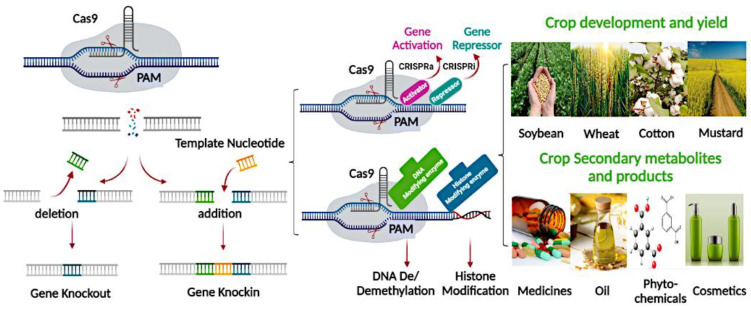
Figure 3.
Application diversity of the CRISPR/Cas system for functional genomic research and crop improvement. CRISPR may directly generate gene knockout (silencing) via deletion or addition with a number of bases and repair through NHEJ depending on the DNA double-strand break mechanism. Alternatively, genome editing may replace an undesirable gene and/or overexpress (knock-in) a single gene when homolog-directed repair occurs with a DNA donor. In addition, CRISPR/Cas may also be employed for base editing, and epigenome editing by deactivating the Cas9 enzyme while using transcription effectors or other enzymes coupled with the dCas9.