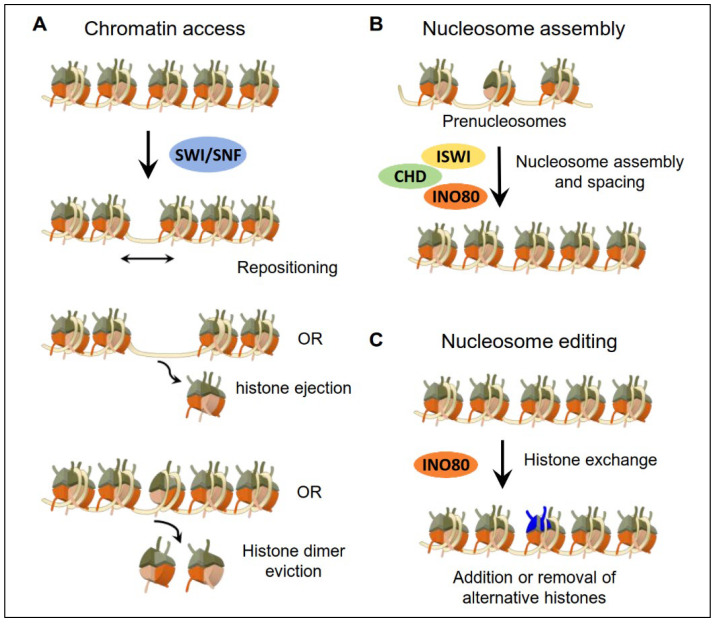
Figure 2.
Brief classification of the functions of chromatin remodelers. (A) Chromatin access: Primarily SWI/SNF subfamily remodelers restructure chromatin coupling ATP hydrolysis via repositioning nucleosomes, ejecting histone octamers or evicting nucleosomes histone dimers. (B) Nucleosome assembly: In particular, ISWI, INO80 and CHD subfamily remodelers re-establish chromatin architecture by the random deposition of histones, the physiological spacing of nucleosomes, and the maturation of nucleosomes. (C) Nucleosome editing: INO80 subfamily remodelers alter nucleosome composition via canonical and variant histone exchange, such as histone variants, as marked in blue.