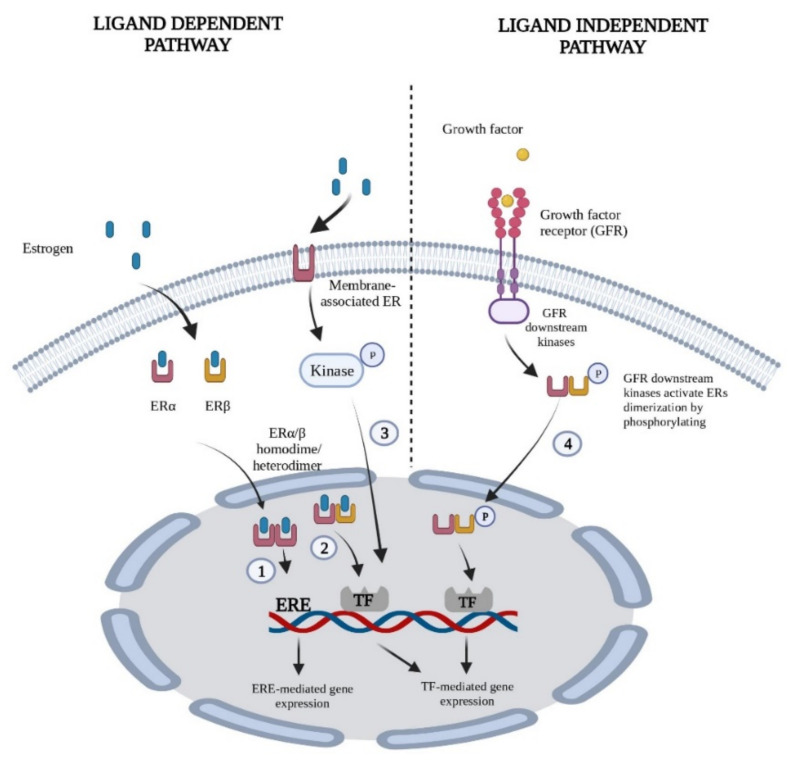
Figure 3.
Illustration of ER signaling pathways. In ligand-dependent signaling, 1: Estrogen binds to intracellular ER and translocates to nucleus for binding to estrogen response elements (EREs) in target gene promoters regulating estrogen-responsive genes, 2: Estrogen binds to intracellular ER and translocates to nucleus for binding to transcription factors (TFs), 3: Estrogen binds to membrane-associated ER and induces signaling molecules, including Src tyrosine kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), PI3K/AKT, and protein kinase C, regulating transcription of target genes by phosphorylating transcription factors. In ligand-independent signaling, 4: Growth factors bind to growth factor receptors (GFR) to activate intracellular kinases. GFR downstream kinases activate ERs dimerization by phosphorylation and regulate target gene expression in absence of estrogen in both ERE-dependent nuclear signaling or by interacting with other transcription factors.