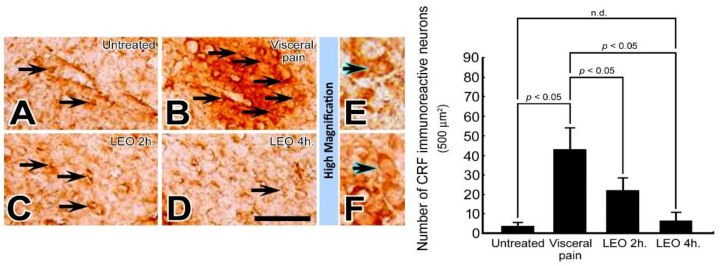
Figure 1.
Photomicrographs (A–F) and histogram show the CRF immuno-expression in the CeA of the untreated (A), visceral pain (B), and OS groups receiving LEO for 2 h (C) and 4 h (D). Note that in the untreated group, nearly no or only a few CRF immuno-reactive neurons were detected in the CeA (A). However, following visceral pain, numerous CRF immuno-reactive neurons with strong staining intensity were detected in this nucleus (arrows, B). Nevertheless, in rats subjected to visceral pain and who received LEO inhalation, the CRF immuno-expression was significantly reduced in which only a small number of CeA neurons were stained with CRF immunoreactivity (arrows, C,D). High magnification (E,F) clearly illustrates the morphological profile of the CRF immuno-reactive neurons (blue arrows) in both untreated (E) and OS group (LEO 4 h.) (F). Quantitative evaluation paralleled well with immunohistochemical findings in which LEO inhalation successfully reduced the number of CRF immuno-reactive neurons in the CeA following the induction of visceral pain. n.d. = no significant difference. Scale bar = 25 μm in (A–D), and = 12.5 μm in (E,F).