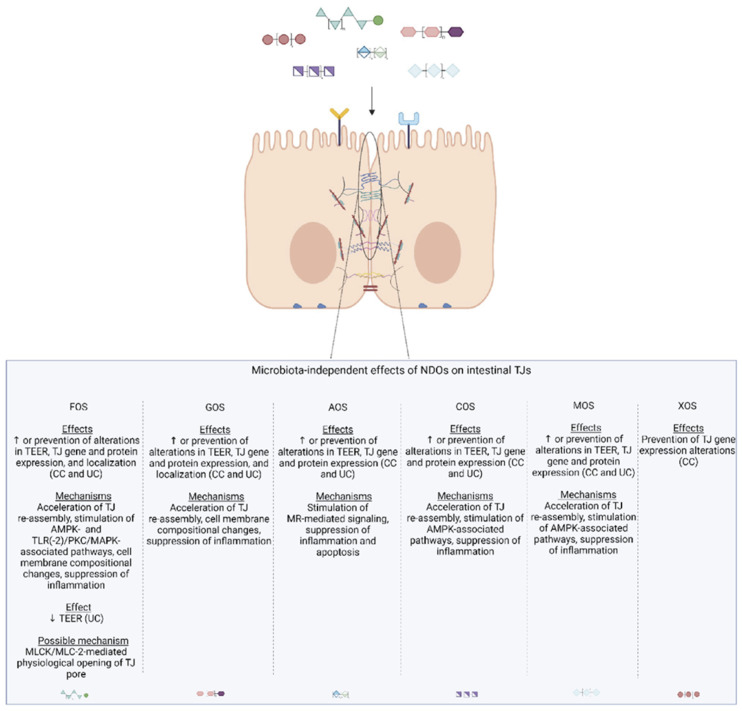
Figure 9.
Synopsis of the NDO-mediated microbiota-independent effects on TJs: Apart from their prebiotic-associated barrier reinforcement, the NDOs interact with cell surface receptors including TLR, CaSR, and MR, positively modulating TJ functionality. NDOs can strengthen and protect the epithelial barrier integrity under normal and pathological conditions, preventing alterations in TJ expression and localization induced by injurious stimuli. These effects can be mediated by stimulation of TJ-regulatory effectors such as AMPK, PKC, and MAPK or by suppressing inflammatory and apoptotic pathways upon direct regulation of IECs and immune cells. CC: challenged conditions: treatment with NDO + a trigger; UC: unchallenged conditions: treatment with NDO solely. Created with BioRender.com. AMPK, Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; CaSR, Calcium-sensing receptor; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinases; MR, Mannose receptor; NDO, Non-digestible oligosaccharide; PKC, Protein kinase C; TJ, Tight junctions; TLR, Toll-like receptor.