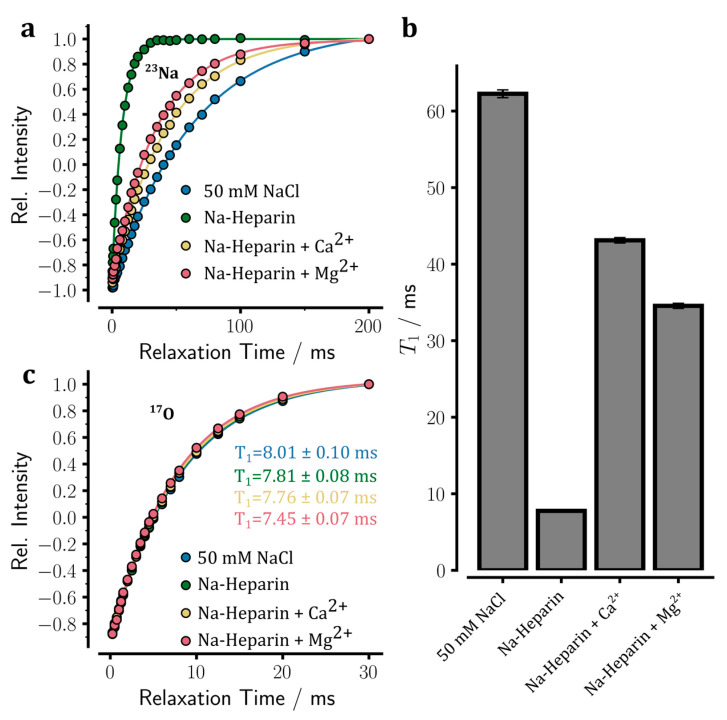
Figure 4.
Longitudinal spin-lattice (T1) relaxation of 23Na NMR signals in sodium heparin samples determined through standard inversion-recovery NMR experiments. (a) The 23Na inversion-recovery data are shown as relative intensity versus relaxation time (duration of relaxation delay) for the following samples: sodium heparin sample without added ion, sodium heparin samples with 100 mM CaCl2 or MgCl2 added, and a reference NaCl solution. Upon the addition of Mg2+ and especially Ca2+ ions, the relaxation-induced recovery of 23Na signals becomes slower and approaches but does not reach, that of the reference NaCl sample. (b) The obtained 23Na T1 relaxation times of the measured samples. The 23Na T1 data show partial Ca2+ or Mg2+ ion-dependent release of sodium ions from heparin, which is stronger in the case of Ca2+ ions. (c) The 17O inversion-recovery data of the above samples show only slight differences in the viscosity-dependent 17O T1 of water.