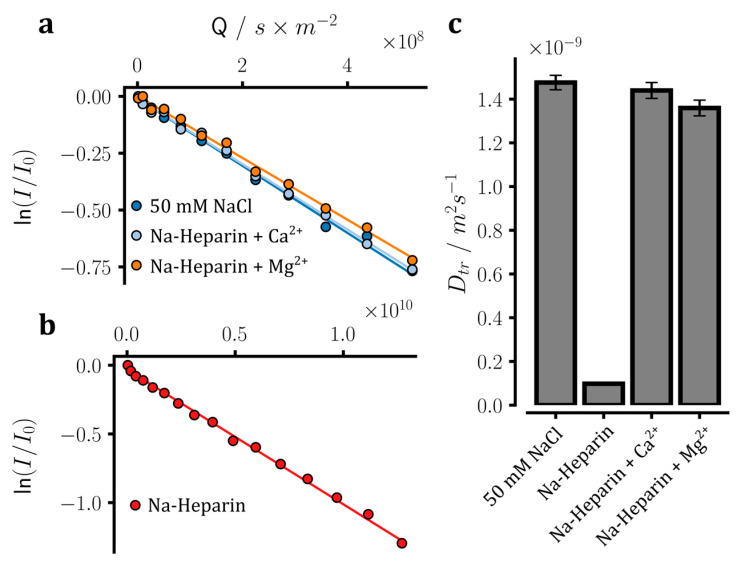
Figure 5.
Translational diffusion of sodium ions measured in heparin samples through 23Na or 1H-based pulse field gradient NMR diffusion experiments. (a,b) Gradient-dependent decrease in the intensity of 23Na NMR signals in sodium heparin samples in the presence of 100 mM CaCl2 or MgCl2, as well as in the reference NaCl sample. Due to the fast relaxation of 23Na signals in the sodium heparin sample without added ions and the severe loss of 23Na signal intensity, no 23Na NMR diffusion experiment could be conducted for this sample. Instead, as shown in (b), the diffusion coefficient of sodium ions in the heparin-bound form was estimated through a 1H-based NMR diffusion experiment, assuming that the heparin molecules and sodium ions are rigidly bound and diffuse together. (c) The obtained translational diffusion coefficients (Dtr) of sodium ions in the measured samples. The diffusion data are consistent with the partial release of sodium ions from heparin after the addition of Mg2+ and especially Ca2+ ions.