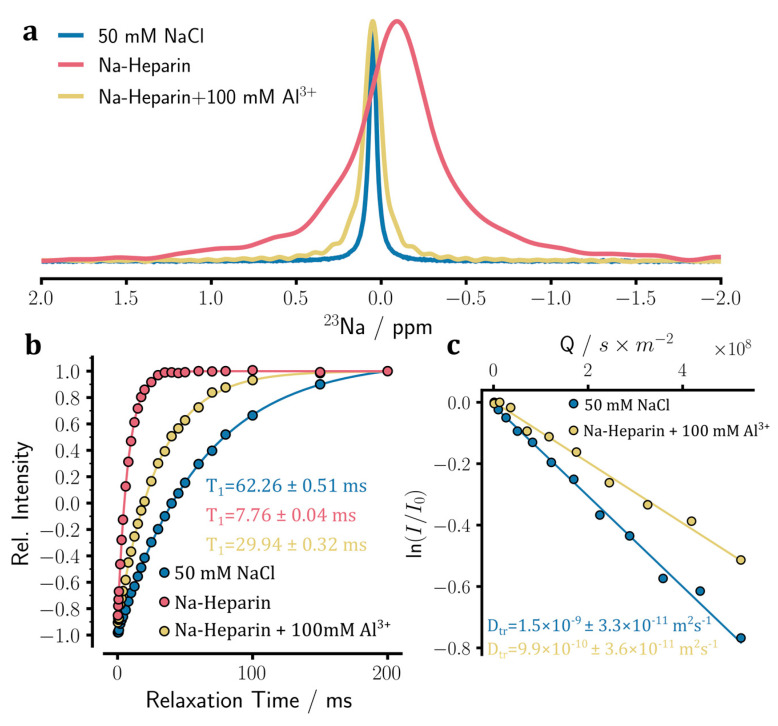
Figure 6.
Aluminum ion binding to sodium heparin was monitored through 23Na NMR experiments. (a) 1D 23Na NMR spectra of sodium heparin, before and after the addition of 100 mM Al2(SO4)3. The spectrum of the reference NaCl solution is also shown. The addition of Al3+ ion leads to 23Na signal narrowing and peak displacement towards the chemical shift of free sodium ions. (b) Longitudinal spin-lattice (T1) relaxation of 23Na signals measured through standard inversion-recovery experiments. The T1 relaxation data indicate the partial release of sodium ions from heparin caused by the addition of Al3+ ions. (c) Translational diffusion coefficient (Dtr) of sodium ions measured through pulse field gradient NMR diffusion experiments. The Dtr of sodium ions in the heparin with Al2(SO4)3 sample is larger than that of the heparin sample without added ions (see Figure 5c) but smaller than that of the reference NaCl sample. This is consistent with the partial release of sodium ions from heparin caused by added Al3+ ions.