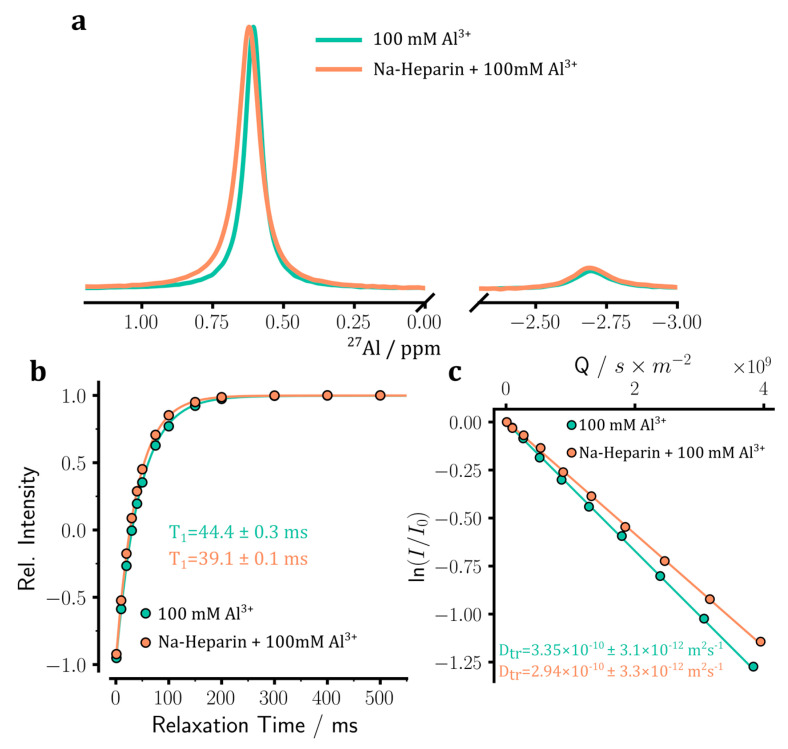
Figure 7.
Aluminum ion binding to sodium heparin was monitored through 27Al NMR experiments. (a) 1D 27Al NMR spectra of 100 mM Al2(SO4)3 sample, in the absence or presence of sodium heparin. The major and minor peaks, respectively, corresponding to [Al(H2O)6]3+ and [Al(H2O)5SO4]+ species, are shown. The addition of sodium heparin leads to slight displacement and broadening of the 27Al signal. (b) Longitudinal spin-lattice (T1) relaxation of 27Al signals measured through standard inversion-recovery experiments. (c) Translational diffusion coefficient (Dtr) of Al3+ ions measured through pulse field gradient NMR diffusion experiments. Upon the addition of heparin, a small decrease in 27Al T1 relaxation time (b) and Dtr coefficient (c) is observed, indicating the partial binding of Al3+ ions to heparin.