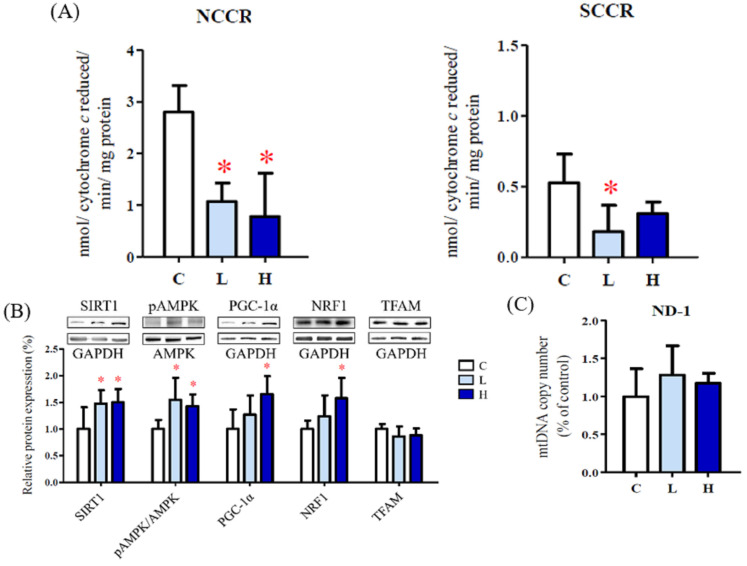
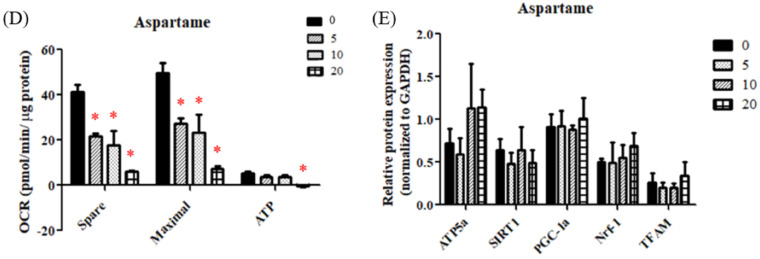
Figure 3.
Effect of aspartame treatment on mitochondrial biogenesis and function in rats and cells. Aspartame upregulates mitochondrial biogenesis as a compensatory mechanism to make up for poor mitochondrial function. (A) NCCR, mitochondrial complex I and III activities and SCCR, mitochondrial complex II and III activities (n = 5). (B) The mitochondrial biogenesis-related protein levels in ovary (n = 5). (C) The mitochondrial DNA copy numbers of ovary (n = 5). Data are normalized with GAPDH. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was monitored using the seahorse XFe-24 analyzer with the sequential injection of oligomycin, carbonyl cyanide-p-trifluoromethoxy phenylhydrazone (FCCP), and rotenone/antimycin. (D) After analyzing, the maximal respiration, spare respiratory capacity and ATP production in KGN cells (n = 3) were calculated. (E) The mitochondrial biogenesis-related protein levels in KGN cells treated with 5–20 mM aspartame for 48 h (n = 3). Data are normalized with GAPDH. SIRT1 (120 kDa); AMPK (62 kDa); PGC-1α (95 kDa); NRF1 (54 kDa); TFAM (28 kDa); ATP5α (60 kDa). All data are expressed as mean ± SD. * p < 0.05 as compared with control. C, control. L, low dose of aspartame. H, high dose of aspartame. NCCR, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide–cytochrome c reductase. SCCR, succinate-cytochrome c reductase. SIRT1, NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase. PGC, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator. NRF1, nuclear respiratory factor 1. TFAM, mitochondrial transcription factor A. ND-1, NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 1. 0, 0 mM; 5, 5 mM; 10, 10 mM; 20, 20 mM.