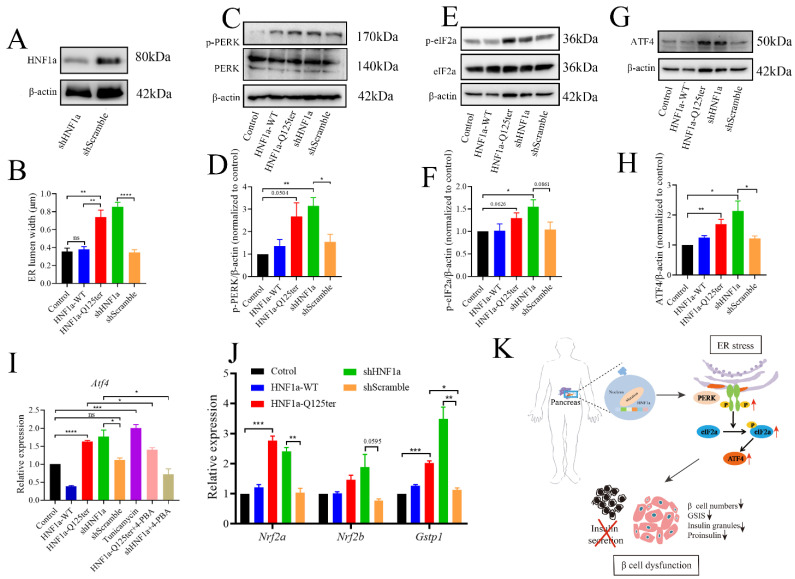
Figure 5.
HNF1a-Q125ter induced ER stress through PERK/eIF2a/ATF4 signaling pathway. (A) Western blot of HNF1a in Ins-1 cells transfected with shHNF1a or control construct for 24 h. (B) Quantification of ER lumen width for control, HNF1a-WT, HNF1a-Q125ter, shScramble, and shHNF1a transfected Ins-1 cells, at least 15 different locations of the same cell were measured, n = 5 individual cells for each group. (C,D) Representative Western blot images (C) and quantification analysis (D) of p-PERK and PERK in different plasmids transfected Ins-1 cell. (E,F) Representative Western blot images (E) and quantification analysis (F) of p-eIF2a and eIF2a in different plasmids transfected Ins-1 cell. (G,H) Representative Western blot images (G) and quantification analysis (H) of ATF4 in different plasmid-transfected Ins-1 cell. Protein levels were normalized to β-actin. (I) RT-qPCR analysis of the expression levels of Atf4 mRNA level in different plasmids transfected Ins-1 cell. The tunicamycin treatment (5 μg/mL) was used as a positive control for ER stress, and chemical chaperone 4-PBA (300 μm/L) was used as an ER-stress reliever. (J) RT-qPCR analysis of the expression levels of Nrf2a, Nrf2b, and Gstp1 mRNA levels in different plasmids transfected Ins-1 cell. (K) Working model for the molecular mechanism of new HNF1a variant resulted in β-cell dysfunction. A schematic that showed how the new variant of HNF1a resulted in MODY3. HNF1a-Q125ter induced ER stress through upregulated p-PERK/p-eIF2a/ATF4 and resulted in β-cell dysfunctions, including decreased β-cells numbers, decreased insulin expression, reduced insulin granules, and impaired insulin secretion. Results are represented as means with standard errors; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001. One-way ANOVA. All experiments were conducted at least three times. WT, wild type; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; PERK, protein kinase R-like ER kinase; eIF2a, eukaryotic initiation factor 2; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4.