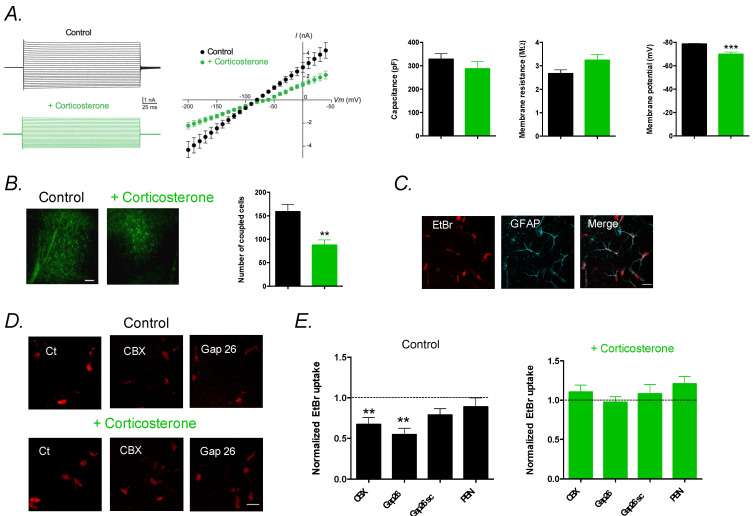
Figure 1.
Chronic corticosterone treatment alters astrocytes’ membrane properties and astroglial connexin functions in the hippocampus. (A) Electrical properties of astrocytes with representative current–voltage (I–V) plots. Data are mean ± SEM of I–V curves, capacitance, membrane resistance and intrinsic membrane properties of astrocytes from control VEH mice (n = 7 cells from 5 mice) and corticosterone (CORT)-exposed mice (n = 8 cells from 5 mice). (B) Representative images and quantification of GJ-mediated biocytin coupling in CA1 stratum radiatum astrocytes from nontreated mice (n = 9 cells from 5 mice) and corticosterone-treated mice (n = 10 cells from 5 mice). Scale bar, 100 µm. Data are mean ± SEM of number of coupled cells. ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001: significantly different from control VEH mice. (C) Representative basal EtBr uptake (red) in stratum radiatum astrocytes labeled with GFAP (cyan) in hippocampal slices. Scale bar, 20 µm. (D) Higher magnification of astroglial EtBr uptake (red) in hippocampal slices from control mice and mice treated with corticosterone, in basal conditions (Ct) and in the presence of CBX (200 µM), or Gap26 (100 µM), applied 15 min prior and during EtBr uptake assay. Scale bar, 20 µm. (E) Astrocytic EtBr uptake normalized to control conditions in slices from untreated mice (Control) incubated with CBX (200 µM, n = 13 slices from 5 mice), Gap26 (100 µM, n = 12 slices from 5 mice), Gap26 scramble peptide (Gap26 scr, 100 µM, n = 13 slices from 5 mice) or Probenecid (PBN, 1 mM, n = 8 slices from 3 mice) and from mice treated with corticosterone incubated with CBX (200 µM, n = 11 slices from 5 mice, Gap26 (100 µM, n = 13 slices from 5 mice, Gap26 scramble peptide (Gap26 scr, 100 µM, n = 12 slices from 5 mice, or Probenecid (PBN, 1 mM, n = 8 slices from 3 mice). Asterisks indicate statistical significance on raw data. ** p< 0.01: significantly different from the basal condition (no treatment) in control mice.