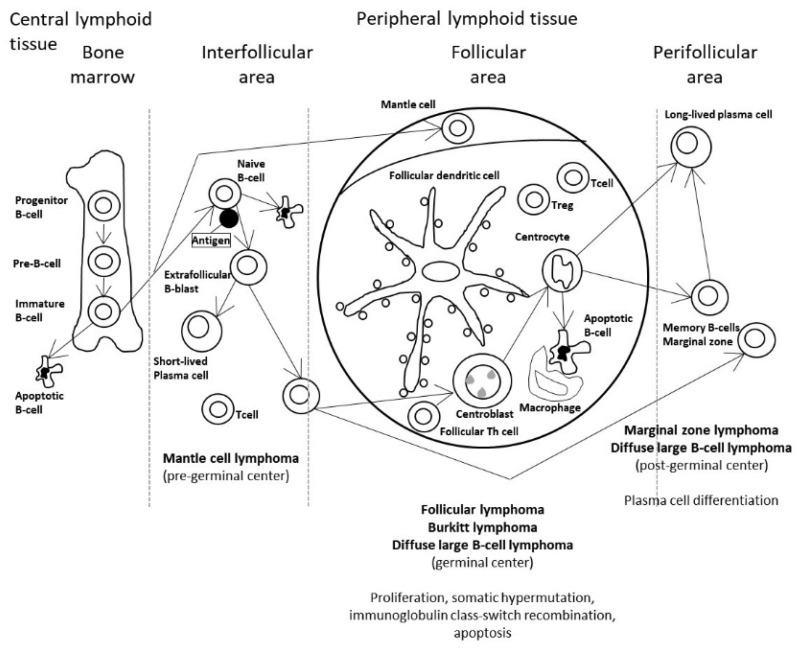
Figure 1.
Postulated cell of origin of the non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. In the current theory of the pathogenesis of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, B-cell neoplasms correspond to various stages of B-cell differentiation. For example, follicular lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma develop (or have a stage of differentiation) from mature B lymphocytes from the germinal centers of follicles of peripheral lymphoid tissues. Of note, follicular lymphoma is characterized by the IGH/BCL2 translocation (t14;18)(q32;q21) that occurs in the bone marrow. Nevertheless, this genetic alteration is not sufficient to generate lymphoma, and additional cumulative changes are necessary.