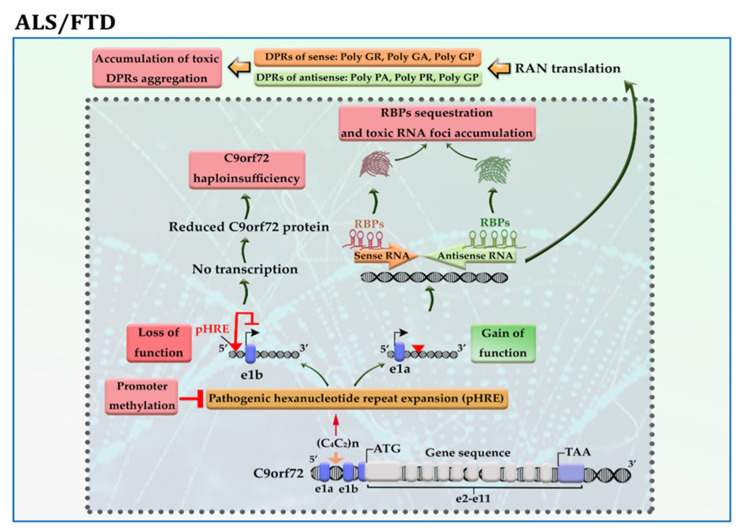
Figure 3.
A schematic representation of the selected mechanisms in the pathogenesis of C9-ALS/FTD. Loss of function; the presence of pathogenic hexanucleotide G4C2 repeats expansion (pHRE) within the promoter region inhibits transcription processes and reduces C9orf72 protein levels. Gain of function; the presence of pHRE within intron 1 leads to the sequestration of RNA binding proteins (RBPs) and the accumulation of toxic RNA foci and dipeptide repeat proteins (DRPs). The promoter hypermethylation of the C9orf72 gene reduces the accumulation of RNA foci and/or DRPs aggregation in the neural cells. Amino acid abbreviations: A: alanine, R: arginine, G: glycine, and P: proline.