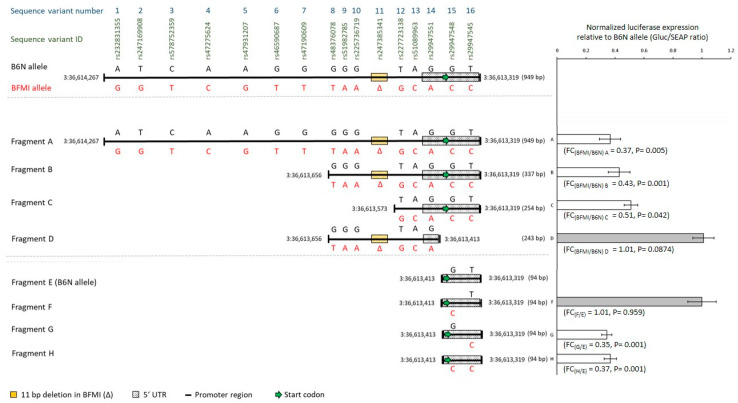
Figure 1.
On the left side, promoter fragments are shown that were tested for their effect on the expression of luciferase as the reporter gene in the dual-luciferase plasmid (ZX-103). The full-length fragment A comprises the whole Bardet–Biedl Syndrome 7 (Bbs7) promoter region of 949 bp between 3:36,613,319 and 3:36,614,267. The 5′ UTR is shown with a patterned black and white box. Fragments B, C, and D are shorter cloned promoter fragments. Fragments E through H (3:36,613,319 to 3:36,613,413) were synthesized. E comprises the shortened C57BL/6NCrl (B6N) haplotype; F, G, and H contain Berlin Fat Mouse Inbred (BFMI) alleles in different combinations. On top, all 16 sequence variants across the promoter fragment are shown with their ID and numbers from 1 to 16. Above every fragment, the B6N alleles are depicted (black), below the BFMI alleles (red). On the right side, a bar chart shows the normalized luciferase expression (GLuc/SEAP ratios) of the tested BFMI promoter variants versus B6N as the reference. Significantly reduced expression was evident for BFMI fragments A, B, and C (FC(BFMI/B6N)A = 0.37, FC(BFMI/B6N)B = 0.43, FC(BFMI/B6N)C = 0.51), but not for D. Testing the short synthesized fragments provided evidence for the importance of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) 16 (rs29947545). The BFMI allele of SNP rs29947545 is required (fragments G and H) for significantly reduced expression (FC(G/E) = 0.35, FC(H/E) = 0.37, FC(F/E) = 1.01). Normalized luciferase expression (GLuc/SEAP ratio) was plotted as mean ± standard deviation of triplicates.