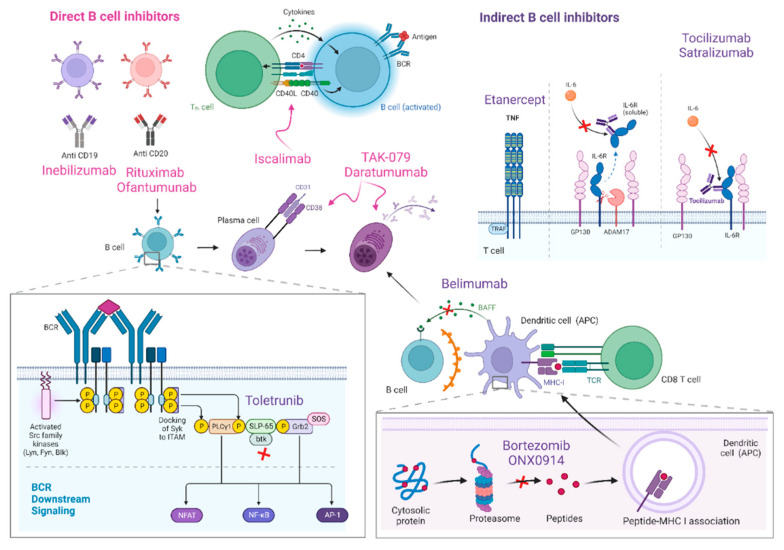
Figure 1.
B-cell inhibitors and their main mechanisms of action are represented in this figure. Direct B cell inhibitors include monoclonal antibodies against CD19 (inebilizumab) and CD20 (rituximab and ofantumumab) B cell surface proteins, as well as iscalimab, a monoclonal anti-body against CD145-CD40. Drugs targeting plasma cells comprise proteasome inhibitors (borte-zomib and ONX0914) and anti-CD38 medications (mezagitamab or TAK-079 and daratumumab). Indirect B cell inhibitors are drugs designed to block IL-6 (tocilizumab and satralizumab), TNF (etanercept), BAFF (belimumab) or BTK (toletrunib).