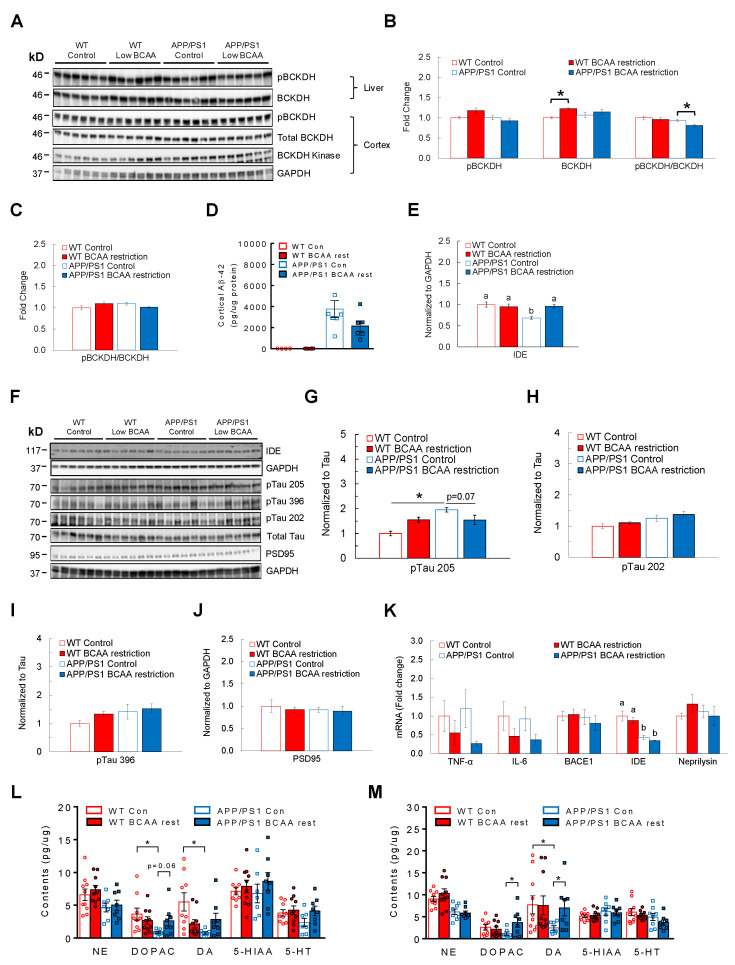
Figure 5.
BCAA restriction lowers brain pathology and restores neurotransmitter content in APP/PS1 mice. 11-month-old WT or APP/PS1 mice without cognitive impairment were placed on a control or BCAA-restricted (50%) diet that is iso-caloric and iso-nitrogenous for two months. (A) Western blots for proteins involved in BCAA degradation in liver and cortex of the brain. (B) pBCKDH and total BCKDH in liver at the end of two months. (C) BCKDH inactivity index (pBCKDH/BCKDH) in the cortex. (D) Cortical Aβ-42 levels normalized to protein by ELISA. (E) Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) in the cortex of the brain. (F) Western blots for IDE, PSD95, and phosphorylated Tau in the cortex. (G) Phosphorylated state of Tau at threonine residue 205, (H) Serine residue 202, and (I) Serine residue 396. (J) Protein expression of PSD95. (K) Analysis of genes involved in neuroinflammation and amyloid production and degradation, normalized to B2M. (L) Monoamine neurotransmitter concentrations in the hippocampus and (M) Cortex. NE—Norepinephrine; DA—Dopamine; DOPAC—Dopamine metabolite; 5-HT—Serotonin; 5-HIAA—Serotonin metabolite. * p < 0.05. Groups with different letters are significantly different from each other with p < 0.05.