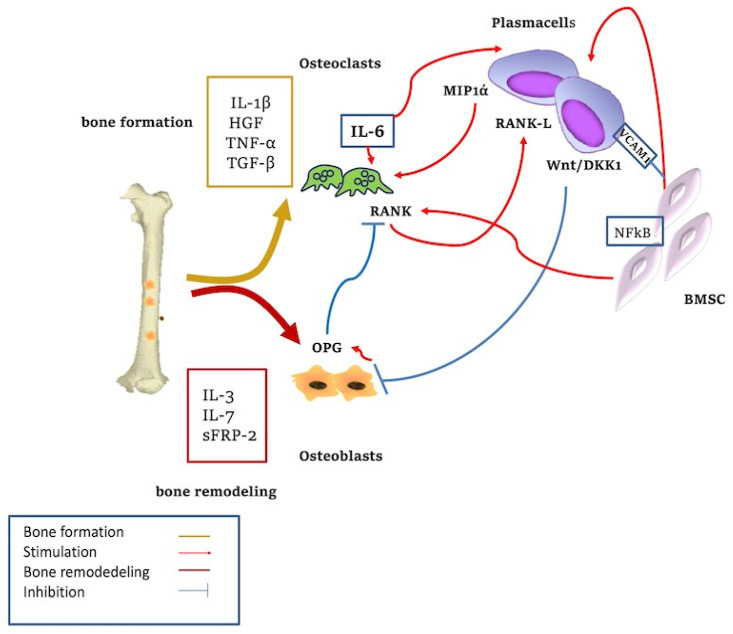
Figure 2.
Cytokine-mediated bone remodeling. The adhesion of plasma cells to stromal cells increases the regulation of IL6 with the activation of osteoclasts. The Wnt/DKK1 pathway is overexpressed in MM-associated lytic lesions. IL-3, IL-7, sFRP-2, and Runx2 are involved in bone formation; HGF and TGF-β act in bone remodeling. Wnt signaling stimulates osteoblasts’ (OB) differentiation. Blockade of this pathway through DKK1 inhibits OB formation. Wnt signaling upregulates RANKL expression from OB precursors, resulting in increased osteoclastic activity and bone resorption. Activation of Wnt pathway increases OPG production from OB which in turn downregulates RANKL-driven osteoclastogenesis. MIP-1α, produced by MM PC, promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoclast maturation. MM cells inhibit the osteoblastic activity through inhibitory factors and reduced production of cytokines.