Table 3.
Chemical structures of cannabinoids and their affinity to the CB receptors.
| Cannabinoid | Receptor Affinity | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Phytocannabinoids | ||
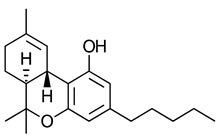 --THC) |
CB1-R and CB2-R agonist | [150] |
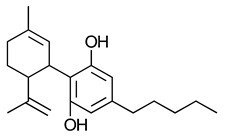 (-)-Cannabidiol (CBD) |
No activity at CB1-R or CB2-R | [150] |
| Endogenous cannabinoids | ||
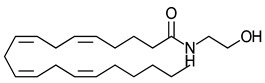 Anandamide |
Greater CB1-R than CB2-R agonist TRPV1 agonist | [104] |
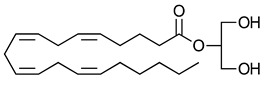 2-Arachidonoyl glycerol |
CB1-R and CB2-R agonist | [70] |
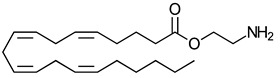 Virodhamine |
Greater CB1-R than CB2-R agonist | [150] |
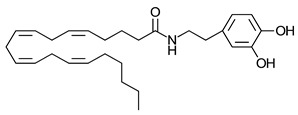 N-Arachidonoyl dopamine |
Greater CB1-R than CB2-R agonist TRPV1 agonist | [150] |
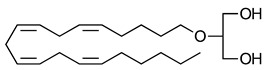 Noladin-ether |
Greater CB1-R than CB2-R agonist | [150] |
| Synthetic cannabinoids | ||
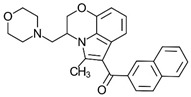 Aminoalkylindole WIN 55,212-2 |
Highly selective CB2-R agonist. | [151] |
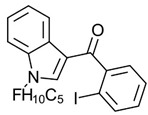 Benzoylindole AM694 |
Potent CB receptor agonist. Highly selective for CB2 receptor. | [152] |
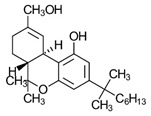 Dibenzopyran HU-210 |
Highly potent CB1-R and CB2-R agonist. Preference for CB1-R receptors. | [153] |
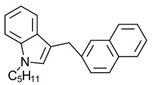 Naphthylmethylindole JWH-175 |
Selective CB1-R agonist. | [154] |
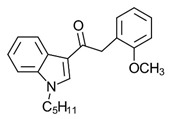 Phenylacetylindole JWH-250 |
Potent CB agonist with greater affinity towards CB1-R. | [155] |
