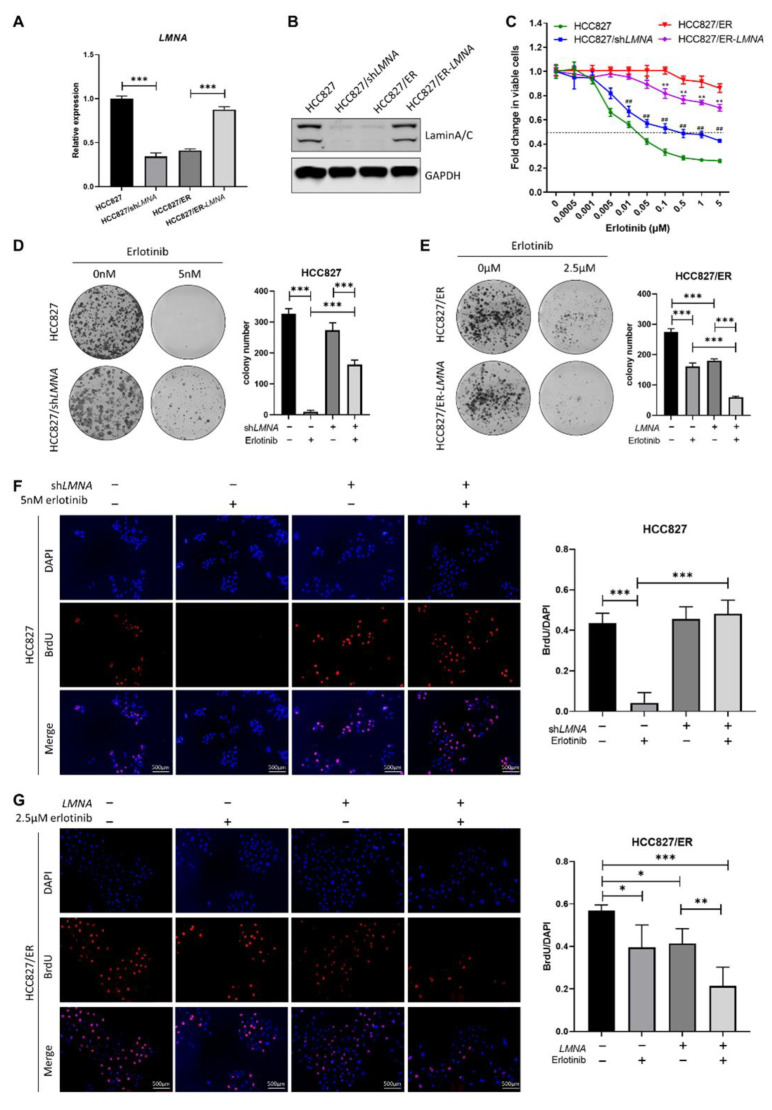
Figure 3.
Effect of LMNA on cell proliferation and resistance to erlotinib in HCC827 and HCC827/ER cells. (A) The mRNA levels and (B) protein expression of LMNA were determined by qRT-PCR and Western blot after lentiviral infections of HCC827 cells with shRNA and HCC827/ER cells with LMNA, respectively. (C) Effect of LMNA knockdown or overexpression on erlotinib efficacy was determined by MTT assay. Data are presented mean ± SD from three independent experiments: ** p < 0.01 versus HCC827/ER cells, ## p < 0.01 versus HCC827 cells. (D, E) A colony-formation assay was performed to investigate the antiproliferation of LMNA in combination with indicated erlotinib in parental and resistant cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Significant differences are indicated as follows: Student’s t-test, *** p < 0.001. (F) and (G) A BrdU incorporation assay was performed in HCC827 and HCC827/ER cells to assess the antiproliferative effect of LMNA combined with 5 nM or 2.5 μM erlotinib after 24 h of incubation, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Significant differences are indicated as follows: Student’s t-test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.