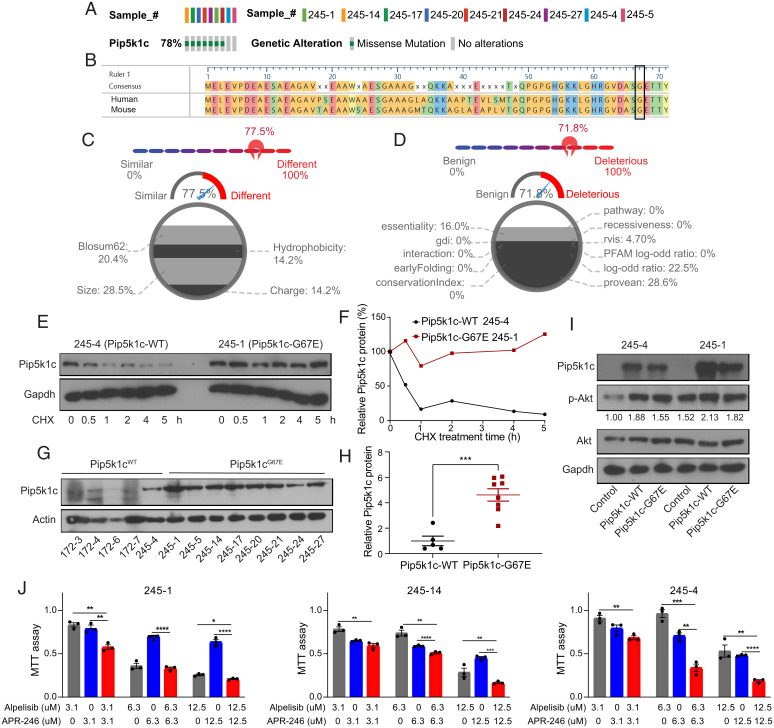
Fig. 2.
WGS identifies a recurrent Pip5k1cG67E mutation activating Pi3k/Akt/mTOR signaling as a potential driver for p53R245W/+ breast tumors. (A) OncoPrint representation of the Pip5k1c mutation identified in Trp53R245W/+ tumors. (B) Alignment of the first 71 amino acids of human PIP5K1C amino acid sequence with mouse Pip5k1c amino acid sequence. Glycine (G) at codon 67 is conserved between human and mouse. (C) Comparison of glycine and glutamic acid in DEOGEN2 generates a score of 0.775, showing the difference between the two amino acids. (D) Human PIP5K1CG67E is predicted to be deleterious and disease causing, with a score of 0.718 by DEOGEN2. (E) Western blot showing the stability of Pip5k1c protein in tumor-derived cell lines treated with 33 μg/mL cycloheximide (CHX) and harvested at different time points. (F) Quantification of the western blot results in E. (G) Western blot showing the protein levels of Pip5k1c in Pip5k1cWT tumors and Pip5k1cG67E tumors. 172–3, 172–4, 172–6, and 172–7 are mouse mammary tumors driven by somatic p53R172H that maintain WT Pip5k1c. (H) Quantification of the western blot results in G. (I) Western blot showing the protein levels of Pip5k1c and p-Akt in Pip5k1cWT and Pip5k1cG67E overexpressing cells with quantification of p-Akt normalized to Akt. (J) MTT assays in 245–1, 245–14, and 245–4 cells treated with alpelisib or APR-246 for 3 d. Results were shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.