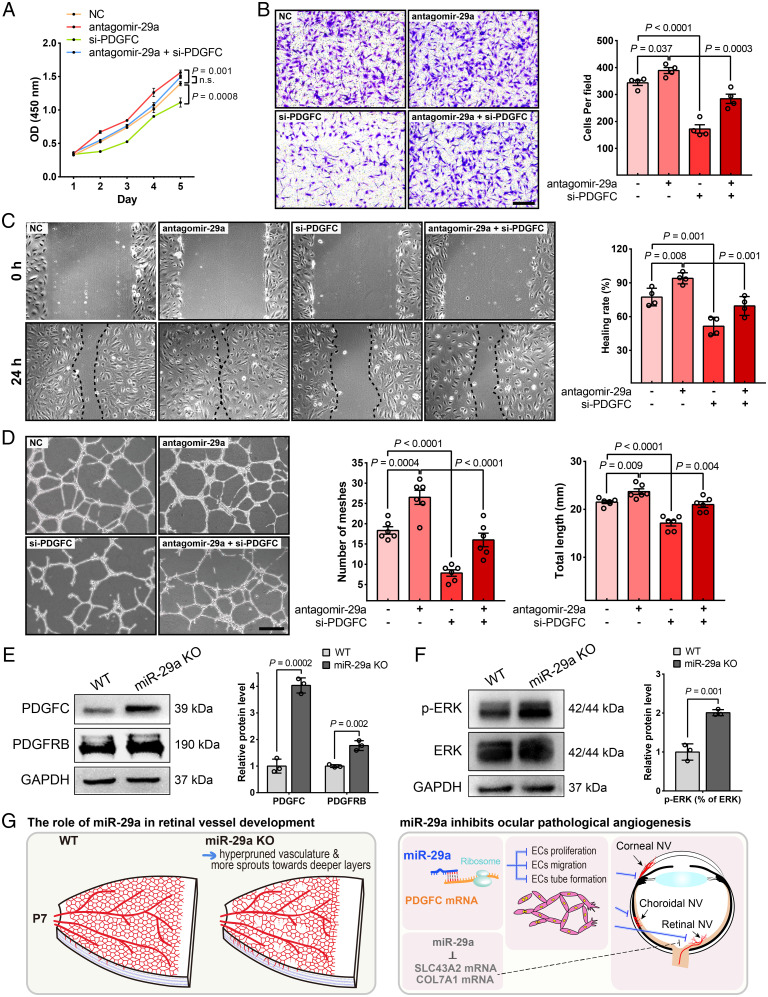
Fig. 8.
PDGFC is an important functional target of miR-29a that modulates HRMEC proliferation, migration, and tube formation ability. (A) PDGFC knockdown markedly inhibited HRMEC proliferation and partially reversed the effect of antagomir-29a on increasing cell viability (n = 3). (B) PDGFC knockdown exerted an inhibitory effect on the migratory behavior of HRMECs, as evaluated using the Transwell assay (n = 4). (C) Down-regulation of PDGFC expression in HRMECs slowed wound closure compared to that in the NC or antagomir-29a group (n = 4). (D) The tube formation ability of HRMECs decreased after transfection with siRNAs against PDGFC (n = 6). (E and F) The protein levels of molecules related to the miR-29a-PDGFC axis in miR-29a KO and WT retinas were detected using Western blot assays (n = 3). (G) Schematic diagram illustrating the mechanism by which miR-29a contributes to ocular developmental and pathological neovascularization (Error bars, mean ± SEM; 2-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test [A], 1-way ANOVA with Holm–Sidak multiple comparisons test [B–D], or Student’s t test [E and F]; Scale bars, 200 μm [B] and 500 μm [D]).