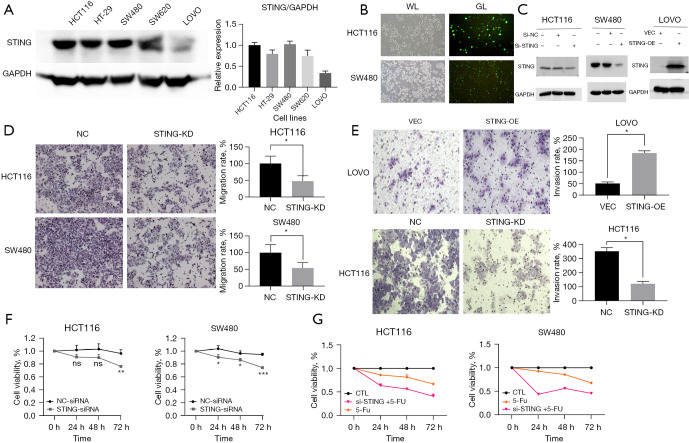
Figure 2.
STING promotes CRC tumor cell growth, migration, invasiveness, and drug sensitivity. (A) Detection of STING expression in CRC cell lines using western blotting; Quantitative analysis of STING expression in CRC cells. (B) Transfection efficiency of siRNA in CRC cells verified by fluorescent siRNA probe (10×, scale: 100 µm). (C) Verification of knockdown and overexpression efficiency using western blot. (D,E) 24 hours after transfection, the numbers of migrating and invasive cells after treatment with NC-siRNA = NC, STING-siRNA = STING-KD, VEC, STING-OE were determined and recorded using transwell assays [3–5 fields were taken for each group, and the results were analyzed quantitatively; Crystal Violet Staining of CRC cells (10×, scale: 100 µm)]. (F) CCK-8 assays were carried out to evaluate the proliferation ability of the cells (HCT116 and SW480 cells) at 24, 48, and 72 hours. (G) The concentration absorbance of each group was measured after 24, 48, and 72 hours using CCK-8 assays for the CTL group, STING-siRNA group, and 5-fluorouracil-treated cell group, and the results was then analyzed and calculated (5-fluorouracil concentration: 2.5 µM). P<0.05 was considered statistically significant; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001. CRC, colorectal cancer; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; OE, overexpression; KD, knock down; VEC, vector; NC, Normal control; CTL, control.